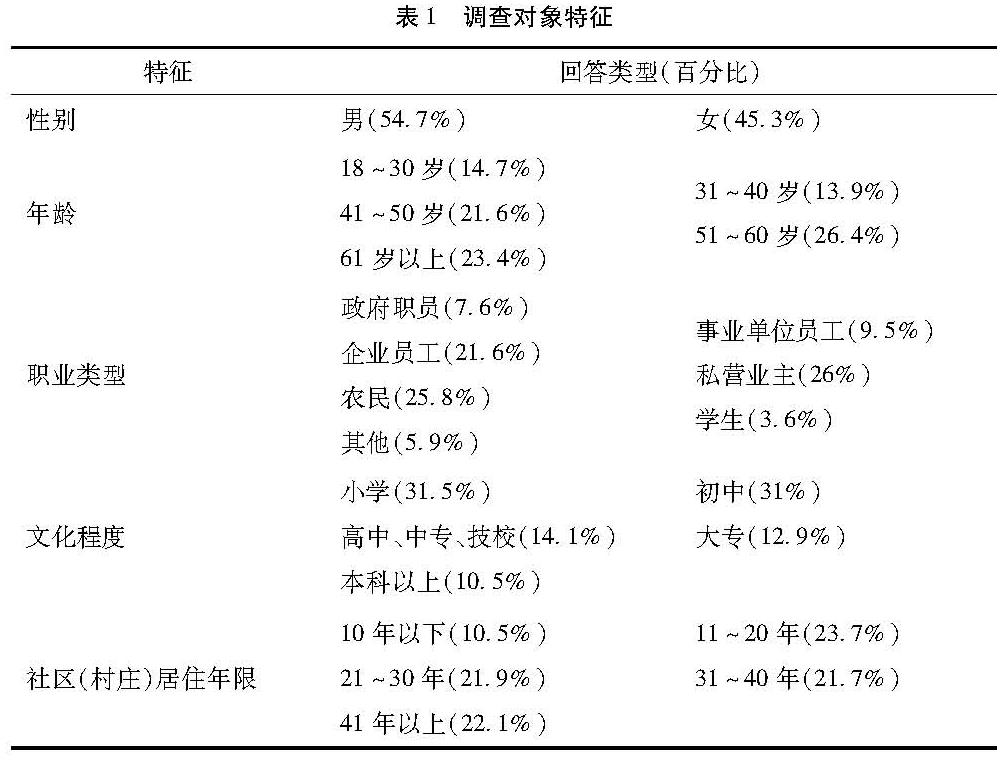
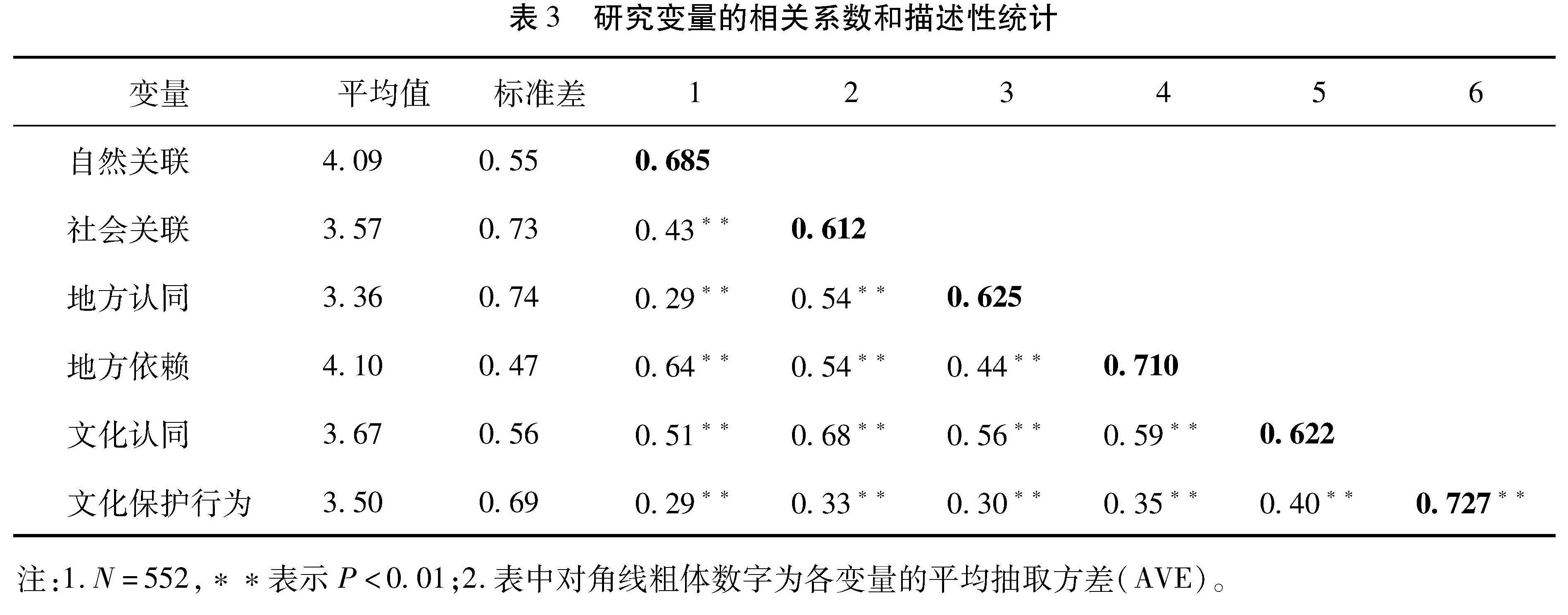
我国各级文化生态保护区拥有丰富的地方传统文化资源,有效促进地方文化的保护与传承是设立文化生态保护区的初衷,也是文化生态保护区建设和发展的核心任务。地方文化的保护和传承离不开各类保护主体的积极作用和保护行为,需要充分发挥各级地方政府、各类社会组织和地方居民在文化保护与传承过程中不同功能和角色。地方居民作为地方文化的主要生产者和传承者,对于地方文化保护和传承最具显著影响。然而,受全球化为典型代表的现代文化的冲击,地方传统文化的保护与传承面临巨大的挑战[1],导致居民对地方文化的认同存在危机甚或缺失的现象。一旦这种现象越来越普遍,将会严重影响居民对地方传统文化保护与传承的意愿及行为。地方传统文化的保护和传承离不开地方居民,缺乏居民保护的意愿和行为,地方传统文化就失去了保护与传承的基础。因此,研究居民文化保护行为的前因机制,有哪些因素对居民的文化保护行为有影响作用,这对于如何加强和激发地方居民文化保护行为,对于文化生态保护区内地方文化的保护和传承,对于文化生态保护区内经济、社会和文化的发展具有重要的实际意义。
国内外相关文献的研究表明当前对于地方文化保护主体和机制的研究主要体现于政府的行为、社会组织的行为、居民个体行为三个层面。从对政府行为研究层面来看,雷玉明等从政府职能的角度阐述了政府在文化保护中的管理角色[2]。Huo Z认为政府构建相关法律制度对文化遗产的保护具有重要作用[3]。Christiane J G也提出政府要通过构建法律制度或条约来保护文化遗产[4]。从对社会组织行为研究层面来看,有研究人员认为非政府组织应通过自身的建设与宣传来发挥其文化保护的作用[5]。J Zhang认为老字号企业是中国传统文化保护体系中的重要组成部分[6]。 Rees H提出地方社区的参与对非物质文化遗产的保护具有重要作用[7]。从对居民个体行为层面的研究来看,董天倩等提出村民、乡村精英是民间传统文化的守卫者[8]。张侃也认为文化保护需要社区民众参与[9]。Kwon H也充分肯定了居民对其社区文化遗产的保护与传承的重要角色[10]。 另外相关研究人员也从政府、社会、居民三者的互动机制进行了研究,诸如吴德群提出国家通过政策职能,建立民间文化保护的制度机制,形成国家、市场、社会互动的有效保护机制[11]。 刘宁也提出了政府主导、市场介入、社会参与的文化保护模式[12]。同时,王纪芒也认为应构建政府主导、民众参与、市场化导向的模式来促进民族文化的发展与传承[13]。
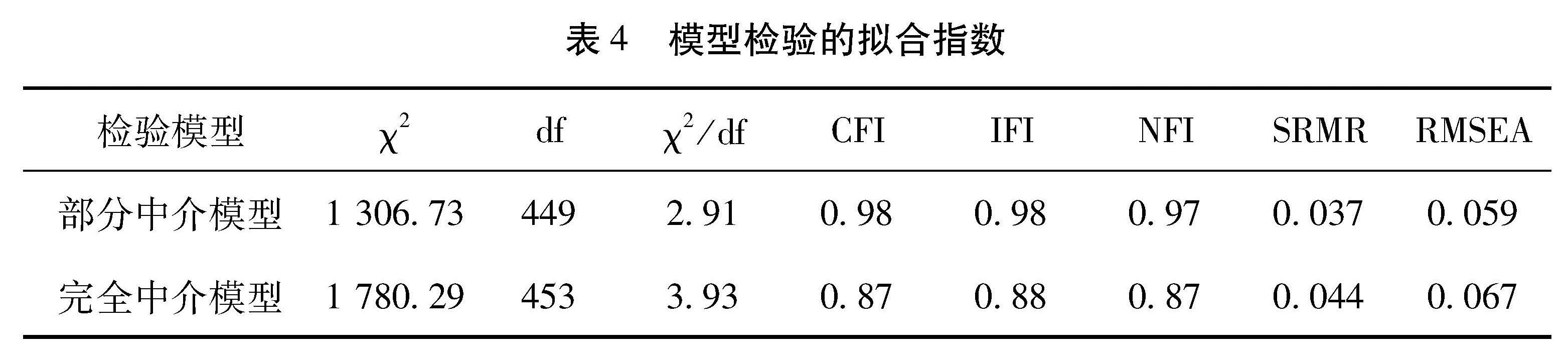
综合以上研究文献来看,主要采用规范研究方法为主,从宏观或中观层面探讨政府、社会、居民三者在文化保护中的角色和相互关系,缺乏对于影响政府、社会、居民三者的文化保护行为内在机制的实证解释。已有研究人员开始运用实证研究方法基于居民的个体层面从情感、认知、利益和政策四个方面分析了居民文化保护行为的影响机理[14]。另有研究也通过实证分析了社区相关因素与居民对文化遗产保护的感知与支持的影响机制[15]。但关于居民文化保护行为的影响因素的研究范畴仍较有限,研究的边界需要进一步拓展。本研究从居民的地方依恋视角来探讨居民文化保护行为的影响机制,通过构建结构方程理论模型回答以下研究问题。首先是地方依恋的四个维度,即自然关联、社会关联、地方认同和地方依赖与居民文化保护行为之间关系的性质是什么?其次是文化认同是否中介了它们之间的关系?
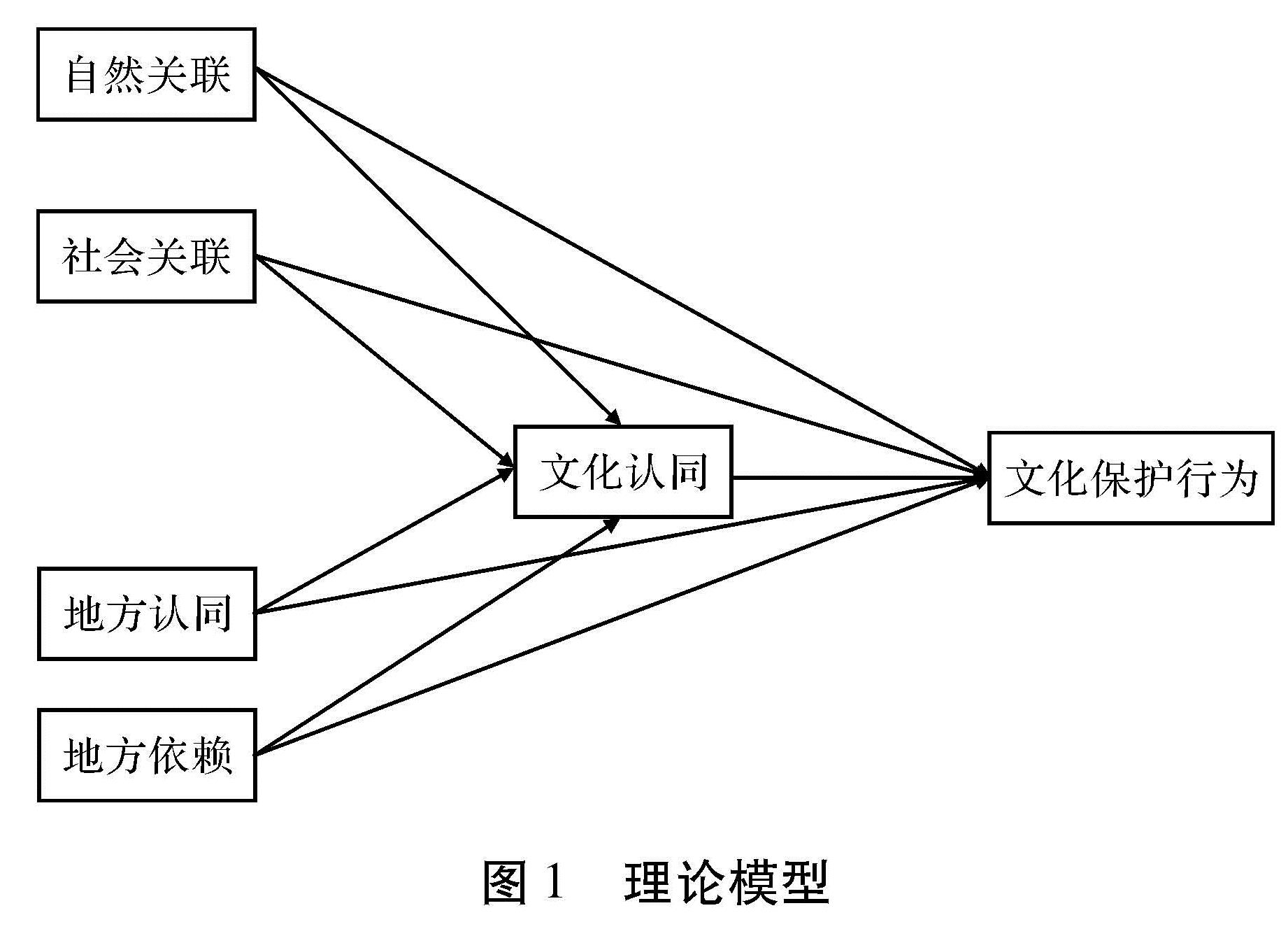
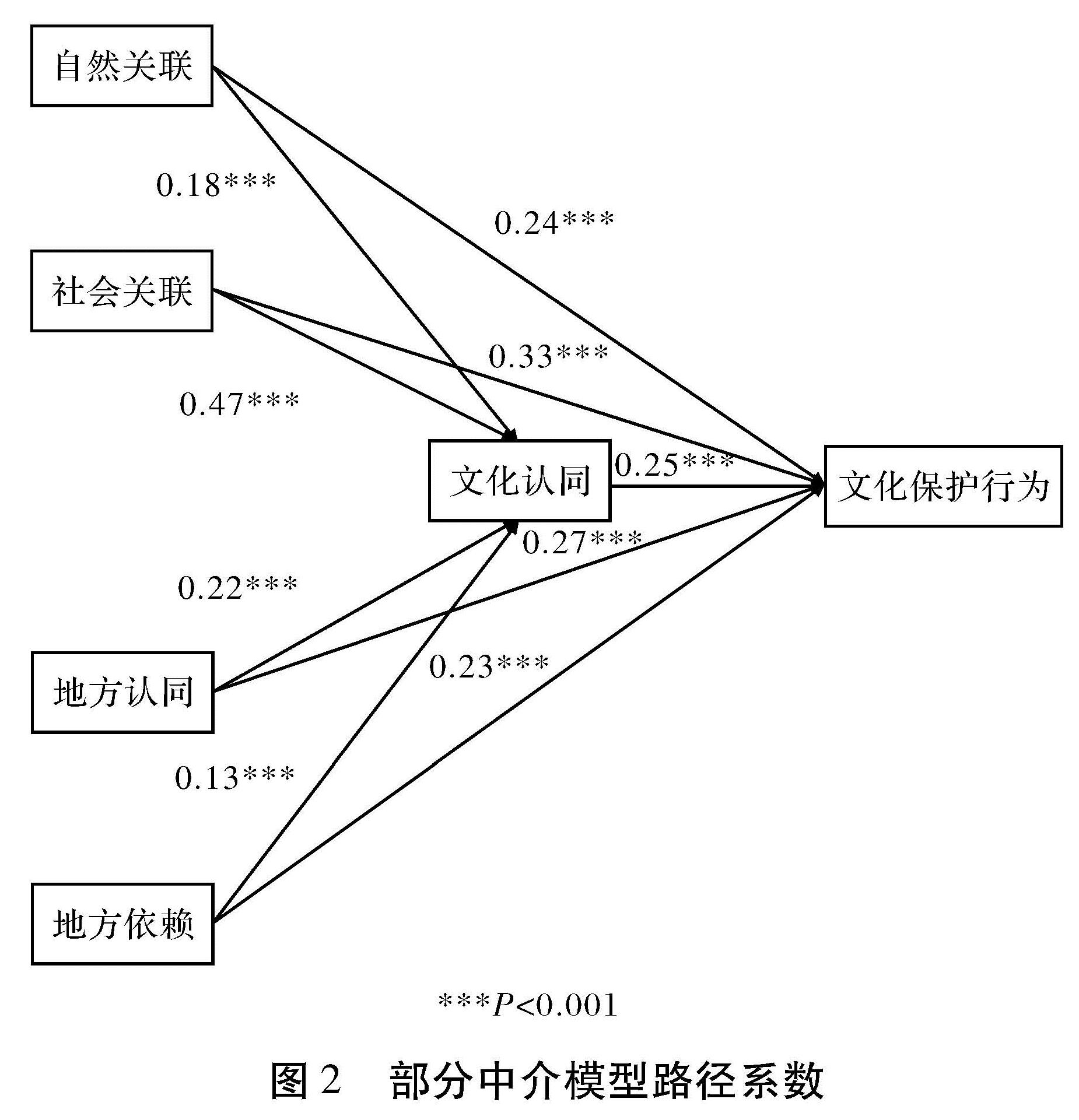
图1显示了本研究的理论模型,该模型表示自然关联、社会关联、地方认同和地方依赖对居民文化保护行为具有直接或间接的效应,表明文化认同是地方依恋的四个维度对居民文化保护行为效应的中介变量。