(School of Business, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China)
emotion; bounded rationality; decision-making; scarcity of mental resources
DOI: 10.15986/j.1008-7192.2019.02.005
备注
情绪的存在是人类有限理性的证据。从神经经济学的视角,探讨人类决策的情绪和情感机制,说明人类如何运用情绪来解决心智资源的稀缺性。情绪是人类拓展有限理性的一种重要机制。情绪介入决策的机制包括情绪的信息优先加工机制、情绪的信息简化机制、情绪的决策参照机制。情绪通过影响或决定决策者的偏好、注意而影响信息加工; 情绪通过“放大”或“缩小”某一信息在决策中的权重而影响决策; “情绪捷径”避开信息深加工而引发决策行动。以情绪作为线索与参照,运用启发式决策模式而实现决策优化等。
The existence of emotions is evidence of human bounded rationality. From the perspective of neuroeconomics, this paper explores the emotional mechanism of human decision-making to illustrate how human beings solve the scarcity of mental resources with emotions. It is believed that emotion is one of the most important mechanisms for human beings to develop the bounded rationality. When involved in decision-making, the emotional mechanism is based on such principles as the priority of emotional information-processing, the emotional information-simplification, and the emotional decision-making reference. Emotions influence the information processing by affecting or determining the preference and mind of decision-makers, and also the decision-makings through zooming in and out of the weights of information if making decisions so that the emotion shortcut triggers decision-makings in the way of simplifying information and bypassing information. The decision-making can be optimized according to emotions as a clue and reference and the heuristic strategy in making decisions.
引言
0 引 言
关于情绪以及情绪与其他过程相互作用机制的研究已经成为认知神经科学的研究热点[1]。认知神经科学证实,情感与理性是人类认知过程不可缺少的两个方面。在复杂情境下,情绪的激活具有适应性优势,增加了人类面对复杂情境的应对能力。
传统经济学认为,人类的基本问题是欲望的无限性和资源稀缺性之间的矛盾,经济学研究资源的配置和利用,这里的资源主要指物质资源。在传统经济学完全理性假设下,心智资源不存在稀缺性。西蒙(Simon,1978)从有限理性出发提出心智是一种稀缺资源。威廉姆森认同西蒙把“心智作为一种稀缺资源的观点”[2],并认为,如果脑力是一项稀缺资源,那么很自然地,人们会节约脑力[3]70。那么人类是如何节约脑力,如何解决有限理性问题的?近10年来,神经经济学研究人脑如何配置心智资源,其目的是运用神经科学的方法证实或证伪主流经济学的观点。
国外学者Dan Hill(2010)从应用角度提出情绪经济学。本文试图探讨情绪如何介入决策,揭示出情绪如何填补有限理性之缺陷而促成了完美决策的机制。
1 情绪和有限理性关系研究简述
西蒙(Simon)有限理性观认为,情景的复杂性,人们要处理并管理大量繁杂的信息。由于人们的信息和认知能力的局限性,不可能是完全理性的。在西蒙看来,人们被情感蒙蔽了判断力,是有限理性的本质之一。情感是负责注意力的机制。它可能唤起或中止我们的注意力。情感的重要性是它能从我们的环境中选出一些特殊的事物,当作我们的注意焦点。情感通过影响注意力来改变你原来思考的焦点,从而影响决策过程。在他的有限理性行为模型中,情感对非程序化决策问题起着相当大的作用[4]127。
西蒙认为,“情感和理智并非天生对立:情感是动机的主要来源,它让我们把注意力集中在特定目标上。而且情感会有助于对其激起的目标进行积极的相关思考。……但是,如果情感很强烈,注意力的焦点就会缩小到一个非常具体且可能只是暂时的目标上,我们也可能暂时忽略在行动前应该考虑的重要因素。所以,在缩小聚焦范围的过程中,情感的确是与理智对立的。”[5]83
行为经济学在西蒙的有限理性观基础上证明了有限理性与情绪的内在关系。他们认为情绪的存在证明了人的有限理性。因为情绪和情感会限制我们思考的范围,“高估”或“低估”某一信息的权重。同时,情绪具有自我实现和自我激励的功能。情绪和情感通过“放大”或“缩小”某一决策选项的吸引力,促使决策者朝着情绪自我实现的方向发展。Slovic(1999)提出运用情感启发式进行决策[6]11。Finucane,Peters & Slovic,Isen & Labroo(2003)认为情绪影响决策质量。Barrya & Olivera(1996)研究了谈判中情绪与决策过程的相互影响。Slovic及其合作者(1999)强调情绪对风险知觉和行为的重要作用。Sally(2001,2002)在博弈实验中发现了“同情”水平对合作和效用的影响。Karnia & Safrab(2002)探讨了个体的公平情绪与行为特征。这些研究从不同的角度探讨情绪如何影响决策。
近年主流经济学有一种新迹象,把情绪作为影响经济决策的一个解释变量,内化到理性选择模型中。其中弗兰克和Schefrin的观点令人注目。他们认为,情绪是有意识的工具理性,是实现长期效用最大化的手段。他们把情绪视为一种理性的战略工具内化,成为理性选择模型的内生变量。将情绪并入理性选择的框架,扩展了理性的内涵。决策者会在情绪的引导下基于长远利益(如因诚实而获得声誉)而忍受短期的损失。情绪调节保证了决策者牺牲短期利益,满足长期利益最大化。因此,情绪是解决和平衡短期利益与长期利益矛盾的一种方法和工具。
针对情感在效用最大化的决策方式中被忽视或实际上被回避现象,阿玛蒂亚·森伦理取向的理性假设从新古典“内核”打开了情感影响经济决策的研究路径。比如人类的道德情感对决策的影响。许多学者试图通过承认情绪所引导的行为目标扩展理性的内涵,从而在理性选择理论的框架内解释爱、同情、公平和合作行为。将情绪并入理性选择的框架,扩展了理性的内涵。它实际上是用理性来解释情绪反应或将情绪反应理性化。这种观点不能解释另一种情形:由情绪支撑的成瘾行为恰恰是人们宁愿牺牲长期利益而追求极端的短期利益最大化结果。
Dan Hill(2010)阐述了情绪的重要性以及情绪在市场和企业中的运用。他把情绪作为一种战略模式,它是指将情绪因素融入经济学中。从操作层面为企业提供一种衡量情绪对人们行动影响力的方法[7]66。我们认为,从操作层面了解情绪的作用非常重要。但需要研究情绪本身以及情绪对决策的影响和作用机制,从理论上说明情绪经济学的基本原理。
2 情绪介入决策机制
情绪是人类缓解、解决有限理性问题的一种方式。情绪经济学(Emotionomics)就是从人类心智运作的角度探讨情绪如何介入决策,说明情绪和情感影响决策的内在机制和作用。它说明人类面对有限理性的现实,是如何运用情绪来解决的。情绪介入决策的内在机制从三个方面体现出来:一是情绪、偏好和选择; 二是情绪与信息; 三是情绪的认知功能。
2.1 情绪与偏好经济学和管理学追求工具理性,而人作为生命存在主要是价值理性。情绪和情感的价值表现为人类生命提供意义和动力,情绪和情感具有价值理性。这种价值理性体现在它决定或影响决策的偏好。情绪和情感可以给决策者带来主观的“收益”或“损失”,具有主观实在性。主流经济学的理性选择模型假设偏好既定。但是在跨期选择、风险和不确定性条件下决策偏好是可变的、不确定的。
情绪影响或决定决策过程有两种可能的方式:一是情绪偏好——决策,其中没有认知加工过程,即情绪就是偏好,直接决定选择和行动。二是情绪——认知(问题编码阶段)——决策。在不确定性和风险状态下,情绪在编码阶段影响预评估,通过改变决策者的偏好而影响选择。基于情绪的某一方案首先影响决策者的风险偏好,最终影响选择结果。因为情绪具有“放大”和“凸现”某方案的价值和吸引力功能,促进决策者选择该方案。也就是说情绪可能使某一方案更加突出,在它在众多备选方案中脱颖而出,最终导致人们选择这一方案。
行为经济学中的框架效应是在风险和不确定性的情况下决策信息的自我编码过程。我们认为,框架效应与情绪有关。不同的表达方式基于不同的情绪框架。同一信息在积极情绪框架下与消极情绪框架下的表达差异会导致不同的决策。获得框架与积极情绪的维持相关,损失框架与消极情绪消除相关。情绪通过影响框架而影响决策。
2.2 情绪的信息优先加工原理情绪的信息优先加工原理主要有两个方面:一是带有情绪性的信息常被认知优先加工。这是由于作为无意识信息加工过程的情绪只需要运用较少的认知资源,通常得以优先加工。
(1)信息加工与情绪
诺曼(Norman D A,1981)认为,人的信息加工系统包括三个部分,即认知系统、情绪系统和调节系统。情绪系统处于认知系统和调节系统之间,成为它们相互作用的桥梁。情绪可以是信息加工的启动状态,也可以是信息加工的背景状态(Dodge & Garder, 1991)[8]15。情绪和情感可以优先加工某一信息,并且赋予某一信息较高的权重。情感是联系非期望和未知事件的纽带,在判断和决策过程中,它有利于信息整合,愿意获取已经在多项目标中给予的优先权[9]。情绪影响信息加工的方式有三种情况。
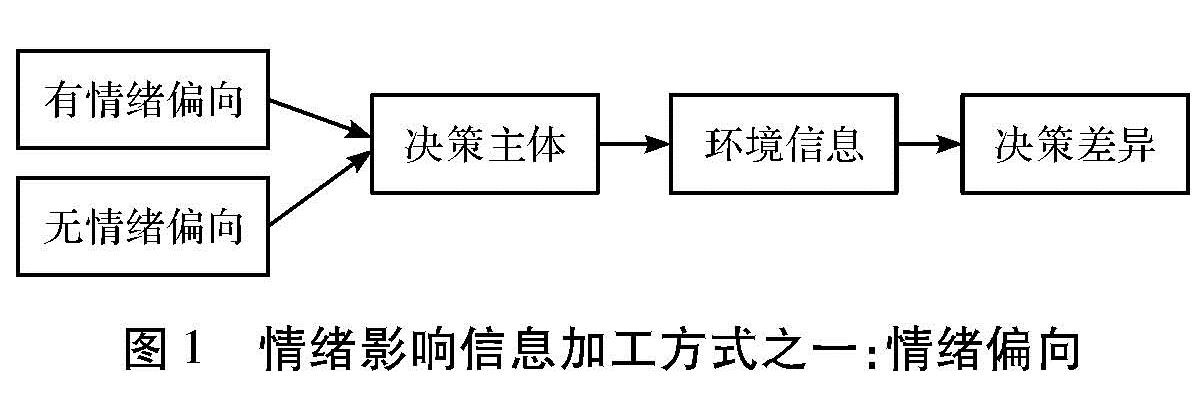
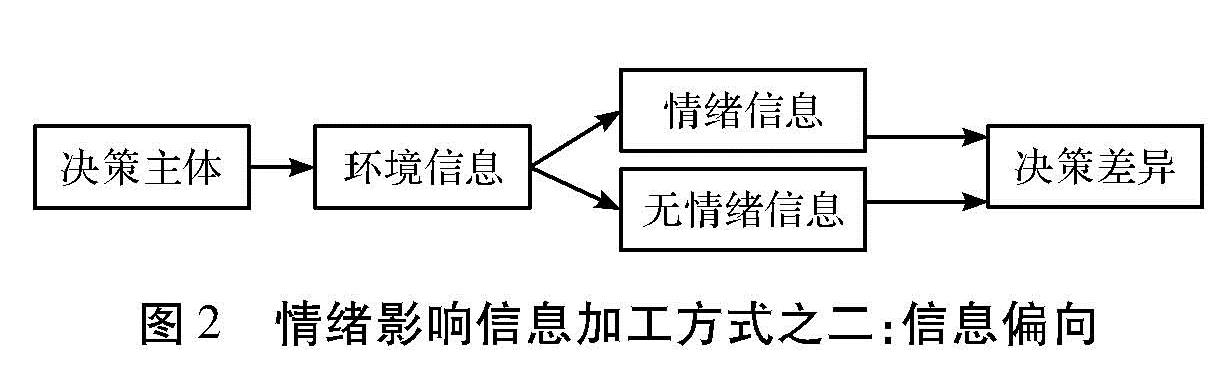
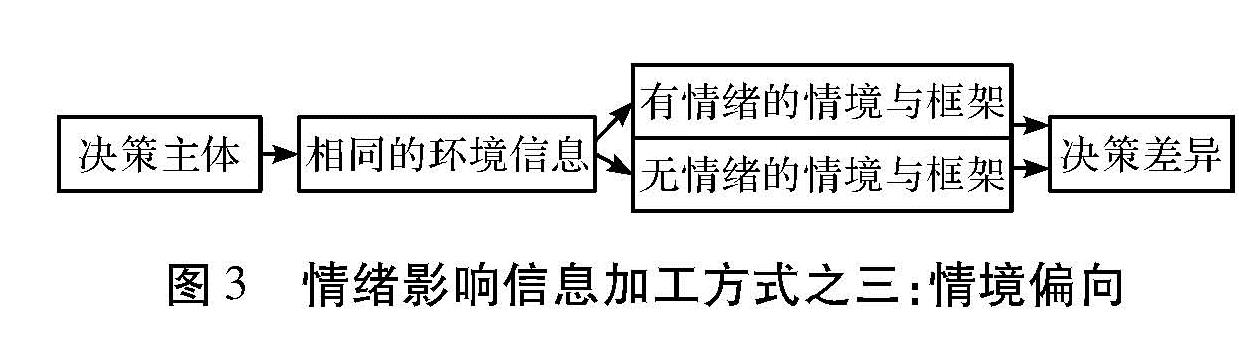
第一种方式,假设信息环境相同,具有某种情绪的决策主体与不具有某种情绪的决策主体相比,信息加工不同。情绪的认知理论认为,焦虑或抑郁个体对与焦虑或抑郁相关的词句不同程度地存在选择性加工偏向(图1)。第二种方式是同一决策主体面对不同的环境信息(情绪信息与无情绪信息)加工不同,通常情绪信息优先得到加工(图2)。第三种方式是同一决策主体,面对的信息相同,但信息的情境和框架不同,一种是情绪的情境和框架,一种是无情绪的情境与框架,最终的决策结果不同(图3)。
第一种是内在的,可能与决策者先天偏好或人生某种特殊的情绪与情感经验有关。第二种与第三种有相似之处。但第二种特指信息的差异性,第三种则强调信息置于何种情境和框架。实际决策中,可能是三种方式的不同组合。这三种方式都说明情绪和情感介入了决策过程和决策结果。
情绪之所以优先加工信息,是因为人类心理过程被分成两个基本的认知过程:自动过程与控制过程。自动过程的特点是:无目的性、无意识性、不可控制性和有效性。显然,一种认知如果不需要控制而自动发生,那么所需要的认知能量将很少。由于心智遵循“节约”的原则,具有自动性特点的情绪和情感常常优先加工。
Svenson 证实了我们的观点。他认为,决策可以分成四种水平[10]287,326。一般决策水平越高,决策所需的能量资源(由心理和生理能量资源构成)就越多。由于人们想尽量少地使用能量资源,因此,在作出决策的条件不变时,人们就会尽量在低水平上做出决策,避免在高水平上做出决策。在决策水平1,个体主义可以通过快速的习惯过程做出决策,决策者意识到决策的情境与早先所经历的情境类似,因此选择以前的类似选项。该水平决策遵守能量保存原则,在日常生活中较为常见。水平2的决策,决策者考虑一个或几个方面的吸引性(包括价值和情感驱动的吸引性),并对各个选项间的吸引性进行比较。水平3的决策过程较为复杂,涉及到各个选项间吸引性(情感和认知价值的)冲突的调整和解决。水平4的决策,决策者面临不熟悉的问题情境,在此情境中创建新的决策选项。卡内曼(2003)区分了认知结构的两个系统推理与直觉。推理是深思熟虑进行的,而且颇费力气; 而直觉思维则似乎自发地进入我们的脑海,不需要有意识地搜寻和计算,因此也就不需要花费我们的精力。直觉和推理这两种认知过程的特征差异被斯塔诺维奇和韦斯特(Stanovich & West,2000)归结为系统1和系统2的中性特征。系统1的运作是快速的、自动的、不费力气的、联想的,并且经常受情感制约。此外,系统1的运作也为习惯所统治,因此很难控制和修改。系统2的运作是缓慢的、连续的、破费力气的,并受制约于深思熟虑的思维。此外,系统2的运作是相对有弹性的,而且潜在地受到规则的支配。
认知神经科学运用fMRI等技术,探索不同情绪决策的脑神经活动,尝试从生理水平上揭示人们的情绪决策过程。根据神经科学的研究成果,人类神经系统在处理信息时有两个过程:受控过程(controlled process)和自动加工过程(automatic process),它们由大脑不同区域产生[11]45。受控过程与意识和认知有关,是基于理性计算的。自动过程与无意识和情绪有关,是基于动机、偏好和情感的。前者信息加工的特点是经过大脑皮层而深加工的,后者信息加工的特点是自动的可以不经过大脑皮层而引发行为反应。在模糊和不确定性状态下情绪和情感系统首先被激活决定决策。情绪和情感的机制是它作为大脑内装置自动进行信息加工。
达奥西莫和Bechara躯体标识假说(somatic marker hypothesis)[12]认为,决策受躯体状态或标识信号所影响,躯体状态来源于生物调节过程,包括情绪和情感过程。躯体状态是由“初级诱发物”和“次级诱发物”所激发。初级诱发物时引起愉快或厌恶的习得状态,而次级诱发物时回忆个人事件或假想的情绪事件而产生的存在物。依据这一理论,几个不同的大脑结构参与引起决策过程中的躯体状态。情绪中枢杏仁核是初级诱发物引起躯体状态的神经系统中的一个关键机制,额前正中皮层(VMPFC)是次级诱发物引起躯体状态的重要机制。杏仁核的反应是突然的并且适应快速,而VMPFC的反应则缓慢和深思熟虑,并且持续时间长[13]。
(2)情绪与注意力
情绪的信息加工优先原理是通过注意力机制完成的。注意是个体进行认知加工的重要条件。情绪通过选择性注意影响认知。有关情绪的理论认为,情绪具有通过集中注意和调整思维,对重要事件进行准备和维持反应的作用,并提供动机和生理能量。Ellis等人的情绪与注意的资源分配模型解释了消极情绪与认知关系。他们认为,在诱发消极情绪的威胁性或危险性刺激出现时,个体的注意资源被高度占用,无暇关注其他,注意范围变窄,当再要求个体完成其他需要占用认知资源的任务时,就出现了竞争,从而污染了认知作业的成绩,尤其是在对注意资源要求较高的认知任务时,思维容易陷入被动刻板[14]。还有学者得出,消极情绪耗费更多的注意资源[15]。消极情绪会污染认知作业[16]。
西蒙认为,情景的复杂性,人们要处理并管理大量繁杂的信息。注意力的集中是我们称之为情感的那些过程的主要功能之一。情感的重要性是它能从我们的环境中选出一些特殊的事物,当作我们的注意焦点。在他的有限理性行为模型中,情感对非程序化决策问题起着相当大的作用[17]127。情感对注意力产生影响,它改变你原来思考的焦点。因此,尽管人们希望理性但达到理想的能力有限[18]34。由于注意力、储存信息以及从记忆中提取信息能力的限制,人们在选择和决策中会借助认知捷径(cognitive heuristics)、情感装置以及既存的知识结构——图式(schema)等来简化策略以提高信息处理与判断决策的速度与效率。
汉诺赫(Hanoch,2002)认为,情绪和理性思考以两种不同的方式共同作用于行为。情绪与理性思考都会限制思考和评价的选择范围,并将人们的注意力集中于特定的信息参数上[19]。情绪一旦被激活,就具有大范围改变大脑程序的能力:改变知觉和注意的方向,改变目标和动机的权重,概念结构的变化,对记忆过程重新定向,改变沟通方式,激活行为规则[20]。
总之,情绪和认知系统是信息加工过程中的两个子系统,所有信息加工过程都含有情绪成分,没有情绪的信息加工是不存在的。情绪的信息优先加工原理说明,行为主体对每一种信息都进行加工,由于情绪和情感的作用,可能会偏好某一信息,而特别地优先加工、自动完成。这样可能导致某一信息过度加工,或者有的信息加工不足。
2.3 “情绪捷径”与情绪启发式决策情绪和情感的作用可节省“理性计算”的成本。人类面对复杂性、不确定性是如何运用有限的心智进行选择,如何降低心智成本的?情绪和情感是如何“延长”理性的?我们认为,是通过简化复杂性和不确定性来“延长”理性。有限理性的决策者在时间压力和不确定性条件下,运用情绪和情感机制自动“删除”或“忽略”某些信息,只选择性加工某些信息。这种情绪和情感决策方式在一定程度上可“弥补”人类理性之不足。它是人类解决有限理性的一种机制,其表现为情绪捷径引发“快速”反应,使行为主体更好地适应环境; 情绪通过选择性注意简化、限定、筛选信息,使决策者不受信息过多的干扰。
(1)情绪捷径
在信息模糊、风险和不确定性状态下,行为主体会启动情绪和情感决策。奈特正是根据“根本的不确定性”解释情感代替理性决策。情绪捷径指情绪“抄近路”,自动、快速地反应和评价环境信息,无需经过大脑皮层深加工,是人类一种应对风险而进化出的信息处理机制。情绪是人类适应环境的自动评价方式。
情绪“走捷径”得到认知神经科学的证实。认知神经科学已经发现,控制情绪的中枢往往压倒理智思考方式。“情绪短路”就是指情绪信息从丘脑抢先达到杏仁核,在新皮层的思维中枢尚不知道的情况下,杏仁核先于理性思维独自激发了原始的情绪反应,这种靠情绪直觉完成的即刻反应,使个体更好地适应环境。关于情绪捷径的路径,我们认同神经科学家Ledoux(1995,1996)的观点。他认为存在两条情绪反射的通路:一条是“低路”,也叫捷径; 另一条是“高路”,即绕行路。两条路相互分离,同时发生。“低路”是刺激的感觉信息先传至感觉丘脑,然后由丘脑直接传送到杏仁核。这条通路绕过了皮层,因此并未对信号进行精细加工,但是这条通路的加工速度更快,可以保证对情绪刺激作出做出迅速反应。丘脑在向杏仁核传递信息的同时也将信息输送到了扣带回皮层和腹内侧额叶等皮层结构进行高级加工[21]576。因此,“高路”的速度虽然稍慢但比“低路”的加工更全面更彻底。情绪可以“绕过”理性直接影响行为。理性离不开情绪,但情绪在某种特殊情形下可以先于理性引发行为。在人类的生存搏斗中进化出一套潜意识情绪系统“先发制人”,在思维中枢没有意识到的情况下,情绪中枢杏仁核先于理性思维独自激发了原始的情绪反应。因此,情绪系统可以不经过大脑皮层直接影响决策和行为。
根据Hsu等(2005)的研究,在模糊条件下,不确定性程度与杏仁核和眶额叶皮层正相关,与纹体系统呈负相关; 且纹状体活动与期望的奖赏正相关[22]。这说明不确定性激活了情绪和情感系统。
(2)情绪和情感的信息简化机制
情绪和情感是一种简化心智活动的方式。人们可以利用情感和建立情感,减少思维活动的“节点”或头绪。从行为选择看,情绪和情感可减少了选择的目标和范围。哈耶克强调,我们在某一刻所知道的关于外在世界的东西是被已经在我们先前的感觉联结中建立起来的分类标准的秩序(the apparatus of classification)所规定的。心灵用记忆的方式把新的感觉与材料同我们的知识储备组合起来。这种活动的结果就是连续的感觉经验的联结网络,哈耶克称之为“感觉秩序”,这种秩序使每一个体能够涉过感觉信息的活生生海洋,而达成理解[23]226,229。
情绪可以简化和筛选信息。人类生存环境的复杂性、信息不完全,特别是人自身行为的不确定,需要一种对信息筛选和删除的装置,以降低心智成本。如果没有一种机制实施“控制”和把握环境,人的行为必将引起混乱。情绪和情感可通过简化思维“节点”或过程,减少不确定性和复杂性。但是,情绪简化的代价是失去大量的信息为基础的。当个体的认知结构形成了世界的秩序时,个体会有意或无意“疏忽”那些与认知秩序相矛盾的信息,而只注意能证实它的信息。
总之,情绪可以集中注意,优先“锁定”某一信息进行认知加工,“删除”无关信息的干扰,从而提高决策效率。情绪的内在机理说明情绪可以弥补人类的有限理性。但不同情绪对认知加工的影响不同。积极情绪可以扩展信息搜索范围,有利于信息的整合; 消极情绪会缩小认知的广度。情绪和情感不仅具有简化信息的功能,更重要的是可以“延长”理性,能一定程度地克服个体的有限理性。
(3)情绪启发式决策
情绪和情感的认知功能指情绪作为决策的线索构造决策的参照点或坐标,减少思维的混沌性和信息搜寻成本。行为主体在认知外界,心智朝向外部世界时,起初对外界是没有建立什么结构和关系的,这时的思维是无序的、混乱的。我们凭感觉、感受和情感来评估周围环境。它是行为的参照点。情绪和情感的“参照”功能可通过认知影响经济主体对新信息的反应和敏感度。Clore & Schwarz提出“情绪、信息等价说”(Feeling as information),认为情绪可以作为一种信息线索直接影响判断[24]323,417。Richard & Gross(2000)表达了同样的观点。他们认为,人们在做出判断的过程中,需要咨询和参考情感池(Affective Pool)。正如可想象性、记忆性和相似性可以作为决策判断的线索一样,情感可以作为许多重要判断的线索[25]。人们常常依赖情绪参照,“一锤定音”决定选择。
总之,情绪经济学的基本原理表明,情绪具有优先加工信息、选择性加工信息、简化信息和决策参考的认知功能。由于它通常是自动的、内隐的和无意识的,节省了心智资源。情绪的脑结构和脑神经机制研究表明,情绪和情感作为一种决策方式,具有大脑生理基础。
3 结 语
人类运用“向外”和“向内”两种方式来解决有限理性问题:制度、习俗、规则、技术、秩序和创新等是“向外”的方式; 认知图式、情绪等是“向内”的方式。这两种方式存在其内在关联。我们的结论如下:
第一,人类面临的主要问题之一是心智资源的稀缺性。人类无限的欲望带来无限的问题,而解决这些无限问题的心智资源是稀缺的。在动态和不确定性环境下如何配置心智资源是经济学需要解决的基本问题。由于人类的有限理性,人类心智存在“节约”原则,其中情绪被视为一种节约心智资源的快捷方式。
第二,情绪影响偏好是通过“放大”和“缩小”功能实现的。情绪影响决策的内在机制表现为“高估”或“低估”某一选项的价值、收益或成本。这是情绪的放大或缩小功能。情绪的“放大”或“缩小”功能对政策分析具有重要的意义。政府和管理者如果欲想推进某一方案,可以对该方案用更积极的情绪描述,会使这一方案更有吸引力,从而人们对它的选择可能性较大。
第三,情绪和情感作用决策的方式需要从心智模型的理解开始。人类是用不同的“内在图式”——心智模型来识别和理解环境的。作为心智模型基本构件的情绪和情感一方面为决策提供内在动力和支撑,更重要的它是一种简化信息加工装置。情绪和情感在认知过程中通过调整和改变“焦点”,“放大”或“忽略”某些信息,简化思维过程。情绪捷径和情绪启发式提高了认知效率。但有时它会“删除”决策所需要的关键信息,导致决策失误。从心智资源的配置角度看,情绪通过影响注意而“抢先”占用认知资源,即情绪能够使注意增加或减少分配对正在从事的认知活动的资源。这样对其它信息可能存在“注意”不足或者“没有注意”。情绪介入决策,在一定程度上拓展了理性,完成了有限理性的超越。
- [1] 周昊天,傅小兰.认知科学——新千年的前沿领域[J].心理科学进展,2005,13(4):388-397.
- [2] WILLIAMSON.Transaction cost economics meets posnerian law and economics[J].Journal of Institutional and Theoretical Economics, 1993(149):99-118.
- [3] 威廉姆森. 治理的经济学分析:框架和意义[M]//埃瑞克·G·菲吕博顿,鲁道夫,瑞切特.新制度经济学. 孙经纬,译.上海:上海财经大学出版社,1998.
- [4] 西蒙.现代决策理论基石[M]. 北京:北京经济学院出版社,1991.
- [5] 西蒙.管理行为[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2004.
- [6] SLOVIC P, FINUCANE M.The affect heuristic[C]//In:Gilovich T, Griffin D, Kaheman D ed. Intuitive Judgment: Heuristics and biases. England: Cambridge University Press, 1999.
- [7] 丹·希尔.情绪经济学[M]. 黎欢,译. 北京:中央广播电视大学出版社,2010.
- [8] DODGE K A,GARDER J. Domains of Emotion Regulation[C]//In J. Garder,K.A.Dodge(Eds.),The Development of Emotion Regulation and Dysreguiation. England: Cambridge University Press,1991.
- [9] GROSS J, JAMES J.Emotion and emotion regulation[C]//In:L.A.Pervin, O.P.John(Eds).Handbook of personality:The Theory and Research.(2nd.Ed.)New York:Guilford,2000.
- [10] SVENSON O. Values, Affect, and Process in Human Decision Making: A Differentiation and Consolidation Theory Perspectives[C]//In: Schneider S.L,Shanteau J.(Eds.).Emerging Perspectives On Judgment and Decision Research. New York: Cambridge University Press,2003.
- [11] LIEBERMAN D R, GAUNT D, GILBERT. Reflection and Reflexion: A Social Cognitive Neuroscience Approach to Attributional Inference[C]//Advances in Experimental Social Psychology. New York: New York Academic Press,2002.
- [12] BECHARA A.Risky business:Emotion, decision-making,and addiction[J].Journal of Gambling Studies,2003,19(1):23-51.
- [13] KENNING P, PLASSMANN H.Neuro economics:an overview from an economic perspective[J].Brain Research Bulletin,2005,67(5):343-354.
- [14] ELLIS H C, ASHBROOK P W. Resource Allocation Model of the Effects of Depressed Mood States on Memory[A]//In: Fielder K, Forgas J.(Eds.)Affect, Cognition, and Social Behavior. New York:Hogrefe,1988.25-43.
- [15] BUODO G, SARLO M, PALOMBA D. Attentional resources measured by reaction times highlight differences within pleasant and unpleasant, high arousing stimuli[J]. Motivation and Emotion, 2002,26:123-138.
- [16] DIBARTOLO P M, BROWN T A, BARLOW D H. Effects of anxiety on attentional allocation and task performance: an information processing analysis[J]. Behavior Research and Therapy, 1997, 35(12):1101-1111
- [17] 西蒙.现代决策理论基石[M].北京:北京经济学院,1991.
- [18] SIMON H A. Models of Man[M].New York:Wiley,1957.
- [19] HANOCH Y.Neither an angel nor an ant:Emotion as an aid to bounded rationality[J]. Journal of Economic Psychology, 2002(23):1-25.
- [20] 庄锦英.论情绪的生态理性[J].心理科学进展,2004(6):809-816.
- [21] GAZZANING M S, IVRY R B,MANGUN G R. Cognitive Neuroscience:The biology of the mind [M]. Second Edition. New York:Norton,2002:537.
- [22] HSU M, BHATT M, ADOLPHS R, et al. Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making[J]. Science,2005(310):1680-1683.
- [23] CHIAKI N, KURT L.The Essence of Hayek[M].Stanford:Stanford University Press,1984.
- [24] CLORE G L, SCHWARZ N, CONWAY M.Affective causes and consequence of social information processing[M]//In: Wyer R S, Srull T K ed.Handbook of Social Cognition.Hillsdale,NJ:Erlbaum,1994.
- [25] JANE M. RICHARDS, JANME J. Emotion regulation and memory:the cognitive costs of keeping one's cool[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,2000(79):410-424.