作者简介:郑 军(1976-),男,安徽财经大学金融学院教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为农业保险与农村社会保障; 张琦雪(1996-),女,安徽财经大学金融学院硕士研究生,研究方向为农业保险与农村社会保障。E-mail:zgja000@qq.com
(School of Finance, Anhui University of Finance and Economics, Bengbu 233030, China)
financial subsidies; long-term care insurance; demand; the proportion of financial subsidies
DOI: 10.15986/j.1008-7192.2022.02.009
备注
作者简介:郑 军(1976-),男,安徽财经大学金融学院教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为农业保险与农村社会保障; 张琦雪(1996-),女,安徽财经大学金融学院硕士研究生,研究方向为农业保险与农村社会保障。E-mail:zgja000@qq.com
引言
第七次全国人口普查数据显示,中国60岁以上老年人口2.64亿,占比18.70%。截至2020年底,我国失能和部分失能老年人口超过4 000万①。2016年7月,《关于开展长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见》正式发布。2020年9月,国家医保局和财政部发布《关于扩大长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见》。财政补贴作为长期护理保险的资金的重要来源,在一定程度能减轻居民的负担,使长护险制度更加合理。因为各试点的财政补贴水平和经济发展状况不同,在提高长期护理保险需求的同时,应该结合多种因素。2021年8月,国家医保局、民政部出台《关于印发〈长期护理失能等级评估标准(试行)〉的通知》。通知旨在推进长护险制度,促进各地区的长护险需求。
长期护理保险需求是在一定的时期内,有长护险需求的人群愿意并且能够购买的长护险的数量。文太林等[1]认为支付能力影响人们对长期护理保险的接受程度和参保热情,对长期护理保险进行财政补贴,能使投保人的可支配收入变多,保费支出能力由此提高,激发投保人积极参与长护险的热情,进而提高长期护理保险需求。荆涛等[2]认为政府补贴支出总额提高,影响长期护理保险的供给,参加长期护理保险的人数会增加。此外,各个省份的发展水平不平衡,这种不平衡也会导致财政补贴对长期护理保险需求的影响不同。因此,本文对此展开研究,有助于分析当前财政补贴对长期护理保险需求是否产生有效的促进作用,从而为提高财政补贴效率并促进基本养老保险制度不断完善起到一定的作用。那么,财政补贴究竟能否提高长护险的需求?财政补贴效率又会对长护险产生怎样的影响?本文将从理论和实际两个方面对上述问题进行研究。
1 文献综述
基于国内外专家学者的研究,目前关于长护险需求影响因素的文献主要集中在经济因素、社会因素、个人因素等方面[3-4]。一是宏观经济因素。为了考察宏观经济指标对于长期护理保险需求的影响,有学者通过实证结果得出,社会医疗保险支出、社会养老保险支出显著对长护险需求的作用明显[5],居民人均可支配收入能提高长期护理保险需求[6-7],国内生产总值也有一定影响[8]。二是社会因素。城镇化水平和老年抚养比对长期护理保险需求的影响都是正向的[9],而财产追回,医护人员,道德风险等因素也影响长期护理保险需求[10-14]。三是个人因素。研究表明,对长期护理保险更了解、认可度高的人群更愿意参与长期护理保险[15],健康状况良好、年轻人和低龄老人参与长期护理保险的意愿更高[16],未来我国长期护理保险的主要目标人是年龄相对较低的老年人[17-19]。
保费补贴对保险需求有明显的促进作用,近些年来,在促进消费支出和增加投保人的可支配收入方面,学者们对财政补贴影响保险需求做了较多的研究[20],要提升补贴效率,就应该优化保险财政补贴机制[21-23]。一是促进消费支出。对于农业保险来说,财政补贴制度有利于整体促进参保农民的家庭消费支出,改善社会福利[24],政府补贴对农业保险需求具有积极且突出的影响[25-26]。各国普遍对其进行财政补贴,目的是推动保险的发展,促进消费支出[27-29]。二是影响投保人的收入。政府参与保险的补贴,有助于增加低收入群体的收入,可以有效缓解贫困[30],财政补贴可以增加可支配收入,缓解居民的购买压力[31-33]。另外,有学者对长期护理保险的筹资问题进行研究,认为应该制定一套具有动态调整机制的补贴政策,掌握主观能动性,根据财政收支情况及时调整补贴力度[34],通过财政补贴来保证资金筹集的可持续性[35-37]。
根据已有文献可知,学者们的研究重点在于长护险的影响因素以及财政补贴对保险需求的影响。但是,鲜有学者把长期护理保险需求和财政补贴放在同一个理论框架下研究两者的关系,此外对于财政补贴效率与长期护理保险需求之间关系的研究也较少。因此,本文主要贡献在以下两个方面:(1)构建了财政补贴下居民长期护理保险消费模型,从理论上分析财政补贴带来的收入、消费对于对长期护理保险需求的影响。理论研究发现,财政补贴通过降低长护险的价格,增加居民的可支配收入,促进长护险的消费。同时财政补贴对长护险供给造成影响,从而对需求有显著的提高作用。(2)利用省级面板数据,通过可支配收入、保障水平等数据实证检验了财政补贴对长期护理保险需求消费的影响。研究发现,从全国层面来看,财政补贴是推动长期护理保险消费的有效动力。分区域来看,财政补贴效率的提高无论是在东部还是在中西部都可以提高长期护理保险需求,而财政补贴效率在中西部地区的促进效果均优于在东部地区的效果。
2 理论模型
在借鉴高旭东等[38]研究的基础上,尝试构建一个在政府干预下的居民长期护理保险消费均衡模型,并由此系统分析财政补贴对长期护理保险需求的影响效应。
2.1 财政补贴支出与长期护理保险需求首先构建长期护理保险的消费模型。在消费均衡模型中,单个投保人的保险效用与社会保险福利同时达到效用最大化,保险市场均衡[39]。由此得到如下的单个投保人长期护理保险消费模型:
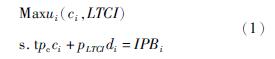
保险市场存在政策性保险,也包括商业保险,二者在市场中并驱争先[40-41]。第i个投保人的保险效用函数为ui(ci,LTCI),商业保险的消费量为ci,di用来表示长护险的消费量,i=1,2,…n,LTCI=∑ni=1di,为长期护理保险的总消费量,且其他保险和长护险的边际替代率递减。pc表示其他保险的价格,pLTCI表示长期护理保险的价格,IPBi是用于保险消费的个人预算。
设U为整个社会的保险福利函数,ηi是投保人在总保险福利中所占的比率,则社会保险福利最大化的长期护理保险消费模型为:
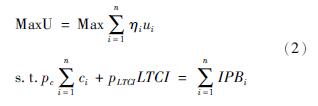
di的函数为:
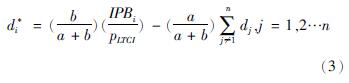
关于政策性保险的消费,我们知道投保人希望自己少消费,他人多消费[42]。d*i的表达式说明,如果投保人断定他人长护险的消费总量越多,自己的消费量就少。长期护理保险的消费总量为:
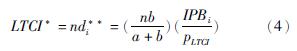
对于政策性保险,如果政府没有相关的措施,对其进行管理,投保人很有可能表现出明显不足的消费能力[43],引导和鼓励投保人自主自愿参保是亟待解决的问题[44]。社会上长护险的消费量不足,这样会降低全社会的保险福利,不可达到帕累托最优。
在政府干预下的最优的长期护理保险消费模型:
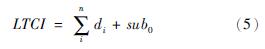
在当前政策下,绝大多数居民选择参与长期护理保险,都是符合经济理性的[45]。政府提供保费补贴,达成了保险价格下降的目的,随之而来的是有效需求的提高[46]。其中sub0为政府提供的长期护理保险的补贴数量,当sub0=0时,总消费量和价格分别是LTCI*和p*LTCI; 当sub0>0时,总消费量和价格分别是LTCI**和p**LTCI。政府为了实现长护险的社会最优消费提供的长护险的总量和总费用F分别是:

我国的长期护理保险存在一定程度的市场失灵[16]。从长期来看,政策性保险的价格和总量存在函数关系[47]。如果用长护险总量LTCI**来确定价格,没有政府补贴,投保人的长护险的消费数量会持续增长,最后超过最优条件,使得保险效用没有办法最大化,增加经济负担; 如果以长护险总量LTCI*来确定价格,在没有政府补贴的情况下,造成长护险的消费量缺乏的局面,使得社会保险福利没有办法最大化。
由此可得到命题1:
H1:财政补贴可以降低长护险的价格,从而使长护险的需求提高。其经济学含义是,在现行的长期护理保险制度下,财政补贴支出额度的增长,可以通过降低长期护理保险价格,提高购买水平,提升投保人的可支配收入,减少投保人承担的保费,从而增加投保人的长期护理保险的消费数量。
2.2 财政补贴效率与长期护理保险需求作为政策性保险的一种,长护险属于准公共产品,兼备公共和私人两种特性[48]。利用效用最大化和消费均衡模型,整体确定长护险保费补贴的补贴数量和补贴金额后,我们可以进一步确定长护险的公共性和私人性的比例。此时的公共性和私人性占比分别为:

式中,KP为公共性占比,KS为私人性占比,KP+KS=1。
这个时候,政府在计算政府实际承担的风险时,其实就是保费实际补贴的风险[46]。对于保费补贴效率来说,这个棘手的难题迎刃冰解,从而促进保险公司等合理使用长护险补贴,提升运用长护险补贴的效能。
由此可得到命题2:
H2:保费补贴效率能够影响长期护理保险的需求。其经济学意义是,财政补贴效率通过影响政府应承担的风险来影响长期护理保险的供给和需求的平衡。
3 变量选择与模型设定
3.1 计量模型为了检验第三部分理论模型中得到的相关命题,研究财政补贴对长期护理保险需求的影响,从第三部分的理论推导我们知晓可以先建立一个回归模型,进行量化分析。鉴于本文的研究目的,为检验理论模型中得到的命题,在式(1)的基础上,设立长期护理保险需求的消费模型:
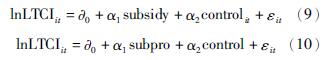
式中,lnLTCIit表示长期护理保险需求; subsidy代表财政补贴; subpro代表财政补贴效率,control为控制变量; εit为随机误差项。若α2显著为正,则财政补贴对长护险需求具有某种正向促进作用。
3.2 变量选取首先,对于因变量选取。相关研究表明65岁及以上老年人口是长期护理保险潜在的、巨大的消费群体。随着年龄的增长,老年人失能的概率会逐渐上升。如果评估长护险的风险,那么相对来说年长的老人长护险的风险系数更大,对护理服务的需求相应扩大。对于社会和家庭来说,老年人口占总人口的比重越来越大,承担的长护险费用也随之增加。与此同时,对长护险需求造成一定的刺激。参考荆涛等[5]的方法,选取城镇65岁及以上人口占城镇总人口比例替代长期护理保险保费收入,衡量我国各地区长期护理保险需求水平。
其次,对于自变量选取。根据文太林等[1]、荆涛等[2]的研究,政府对长期护理保险的财政投入中有很大一部分投向了服务提供方,如长期护理机构建设和社区,长期护理服务组织等,包括开办补贴和日常运营补贴。因此,本文分析财政补贴对长期护理保险需求的影响时,将开办补贴和日常运营补贴之和作为自变量。
最后,在控制变量上,本文选取老年人口抚养比[5]、居民人均可支配收入[3]、养老保障水平[15]、国民生产总值等指标[16]。在社会人口因素方面,选取老年人口抚养比。在宏观经济因素方面,选取居民人均可支配收入、养老保障水平、国民生产总值等指标。居民可支配收入选取省级人均可支配收入对数lnPi,老年人口抚养比用各省老年人口抚养比对数lnOdr表示,养老保障水平用各省城镇医疗保险基金和城镇养老保险基金支出之和对数lnWel表示。考虑到省级层面经济差异的影响,选取地区GDP,各省人均国民生产总值用lnGDP表示。
3.3 内生性问题财政补贴可以促进长期护理保险的需求,而长期护理保险需求旺盛的地区又会得到更多的财政补贴促进消费。考虑到财政补贴和长期护理保险之间存在双向因果关系,从而引发内生性问题。参考田勇等[50]、李佳等[51]的思路,选取中央彩票公益金中的老年人福利预算支出,作为衡量财政补贴的工具变量。中央彩票公益金使用遵循福利彩票“扶老、助残、救孤、济困”的发行宗旨,用于资助为老年人、残疾人等特殊群体提供服务的社会福利项目和其他社会公益项目。老年人福利预算支出通过提取彩票发行销售收入中的一半,按一定比例用于支持养老服务,在长期护理服务项目每年有大量的支出。
从外生性角度看,老年人福利预算支出的数据具有可观测的特点,不直接对长期护理保险的保费进行财政补贴,主要用于长期护理保险机构等的基础设施建设,满足工具变量外生性条件。从相关性角度看,长期护理保险机构的财政补贴的一部分由老年人福利预算支出组成,用于支持发展长期护理保险服务业。老年人福利预算支出属于中央彩票公益金与财政补贴相关,这又满足工具变量的相关性条件。由此可见,选择各省的老年人福利预算支出作为财政补贴的工具变量,基本满足变量的相关性和外生性条件。
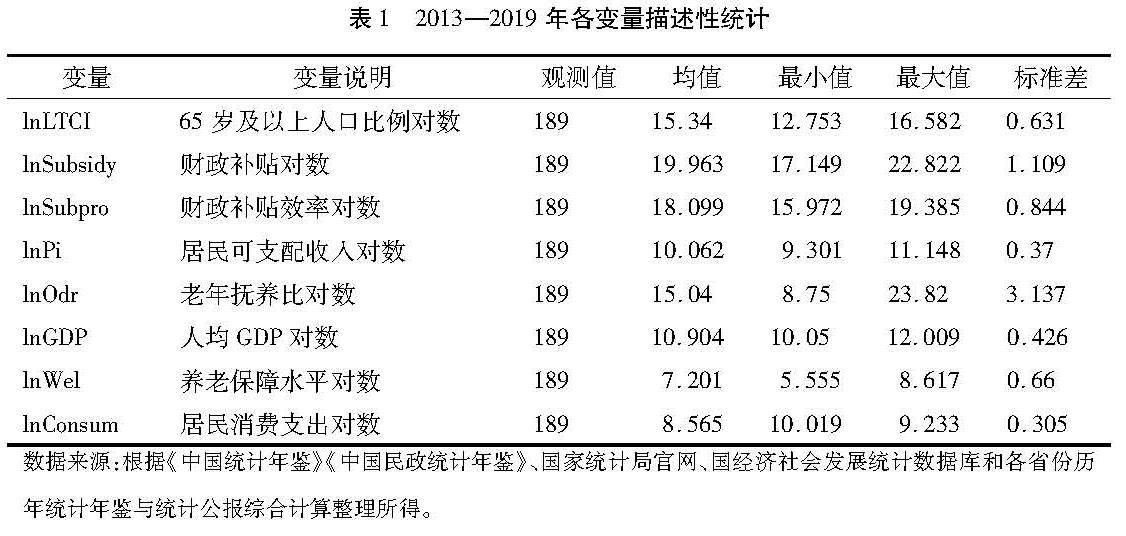
3.4 数据来源与统计特征因长期护理保险制度并未在全国普及,部分数据缺失与相关统计数据的不可获得性,本文将样本确定为具有长期护理保险的27个省2013—2019年的面板数据。所有原始数据均来自《中国民政统计年鉴》《中国统计年鉴》、国家统计局、中国经济社会发展统计数据库和各省份历年统计年鉴与统计公报整理,选取有关因变量和自变量的相关数据。2013—2019年我国27个省市的各变量的原始数据的统计特征(表1)。
4 模型估计与结果分析
4.1 财政补贴支出对长期护理保险需求的影响利用对2013—2019年我国27各省市面板数据(相关变量为189个)进行处理,结果显示,财政补贴与长期护理保险需求密切相关。在进行实证分析时,为了更好地消除可能存在的异方差和对模型结果进行合理分析,对模型中的所有变量都采用对数处理,并据此对财政补贴对长护险需求的影响进行实证分析。本文模型均接受了Hausman检验,判断是选择固定效用还是随机效用模型,得出固定效应模型结果更好。
(1)模型结果描述。在基本回归模型中,基于式(9),利用整理的面板数据,进行固定效应模型回归以及两阶段回归模型处理内生性问题检验财政补贴对居民可支配收入的影响,具体回归结果如表2所示。财政补贴可以对居民可支配收入有正向的促进作用。
财政补贴与居民可支配收入显著正相关,即财政补贴可以有效提升居民的可支配收入,提高长期护理保险需求,这也与假设1的结果一致。但这种影响效果随着地区人均GDP的改变存在着差异,也即是地区经济水平不同影响着财政补贴的效果。地区经济较为发达地区的居民有着较为迟缓的收入增长效应,而地区经济较为落后的居民有着明显的收入增长的效应。
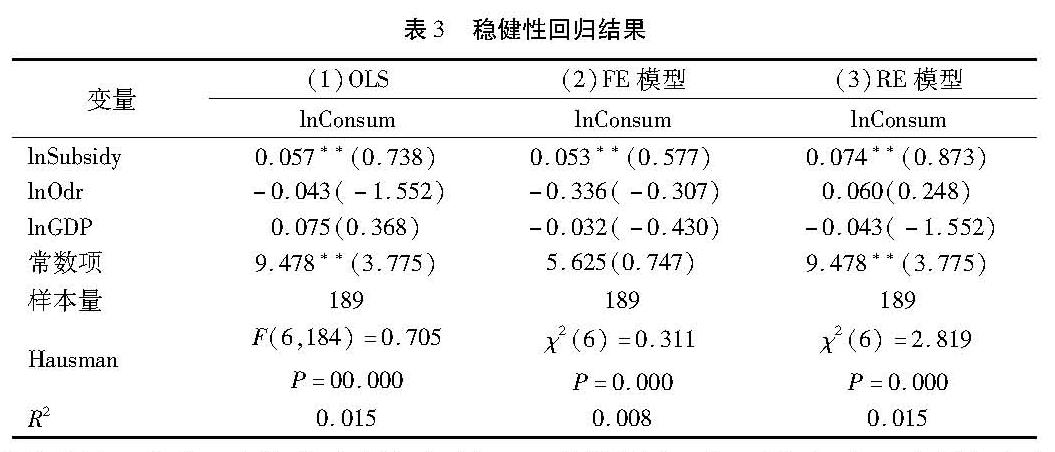
(2)稳健性检验。为进一步验证直接财政补贴对居民可支配收入的促进作用,表3利用居民消费支出替代农村居民可支配收入。从表3可见,财政补贴在模型0LS、固定效应回归结果均显著且为正,其与表2回归结果基本一致,进一步验证了假设2财政补贴促进居民可支配收入增长的作用。回归结构显示,财政补贴会使居民可支配收入增大,促进长期护理保险消费,进而增加长期护理保险需求。
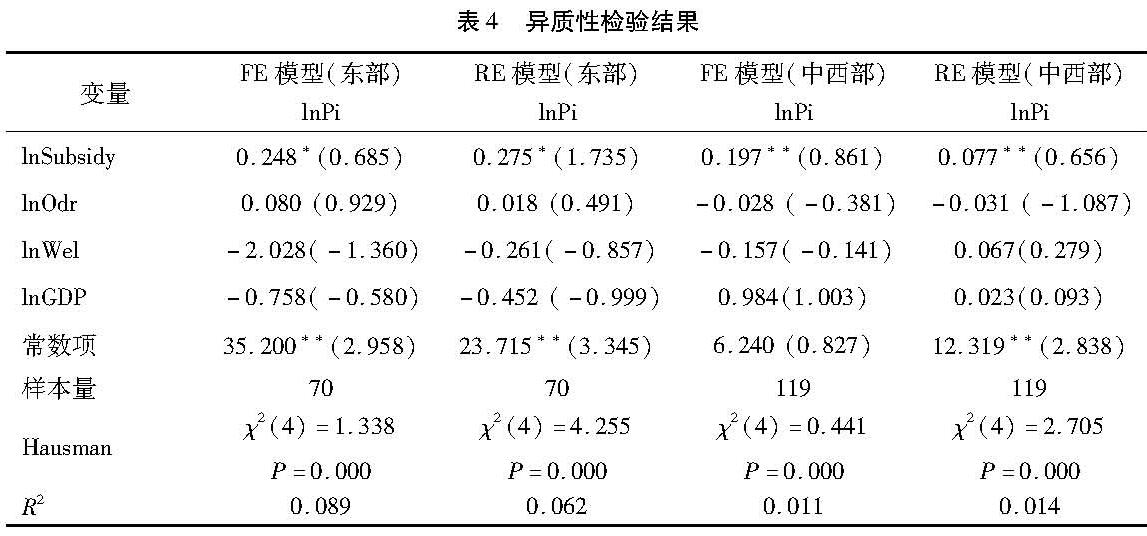
(3)异质性分析。为进一步检验财政补贴对长期护理保险需求的影响,将全部省份分为东、中、西三个部分,然后分别进行回归分析,回归结果如表4所示。中西部地区财政补贴对于长期护理保险需求的结果显著,而东部地区财政补贴对于长期护理保险需求影响的显著性低于中西部,因此财政补贴对于长期护理保险需求的影响在中西部更加明显。
(4)模型结果分析。首先,通过模型结果与模型检验结果来看,财政补贴支出与居民可支配收入之间显著正相关,也即是财政补贴(lnSubsidy)可以有效刺激居民人均可支配收入(lnpi)的增加,这与理论推导部分假设2结果财政补贴可以增加居民可支配收入效应一致。根据 2020 年国家医保局公布的统计数据,中国基本医疗保险参保人数达136 100 万人,占全国总人口的比例为 96.4%②。截至2021年8月,所有的长护险试点,参与长护险的人数合计达1.34亿人③。长期照护包含在笼统的养老服务政策之中,随着养老服务供需矛盾日益突出,政府相继出台促进养老服务业发展的政策、持续增加养老服务的财政投入[1]。2019年,国务院发布了《关于推进养老服务发展的意见》,在保障人人享有基本养老服务的基础上,有效满足老年人多样化、多层次的养老服务需求。政府投入大量资金,为老年人的服务产业做出了较大的努力。其次,补贴对不同地区居民可支配收入的增长作用有显著区别,就经济较为发达地区而言,财政补贴的作用效果不甚显著,几乎为零; 就经济较为落后地区而言,影响较大。经济较为发达的东部地区居民可支配收入主要来源于工资收入; 经济较为落后的中西部地区农村居民收入主要来源为风险较大的经营性收入。我国经济较为发达地区居民的可支配收入并不过分依赖于财政补贴,而经济较为落后的东西部地区则较为依赖。所以财政补贴对于经济较为发达地区居民而言,这种“补收入”的作用效果微乎其微,而对经济较为落后地区则“补收入”则显得尤为重要[50]。不仅要提高长护险需求,还要逐渐扩大长护险的覆盖面,全面提升长护险的补贴效果。试点城市一方面鼓励了居民参保,另一方面引导护理体系和行业的发展,让长期护理的供给和需求矛盾得到缓解。截至2020年底,长护险的试点覆盖人群约1.1亿人,基金收入200亿,受益人136万人受益④。在老龄化程度加深的背景下,长护险享受待遇人群的扩大、给付标准的提高都有赖于相对独立的多元筹资体系的建立。
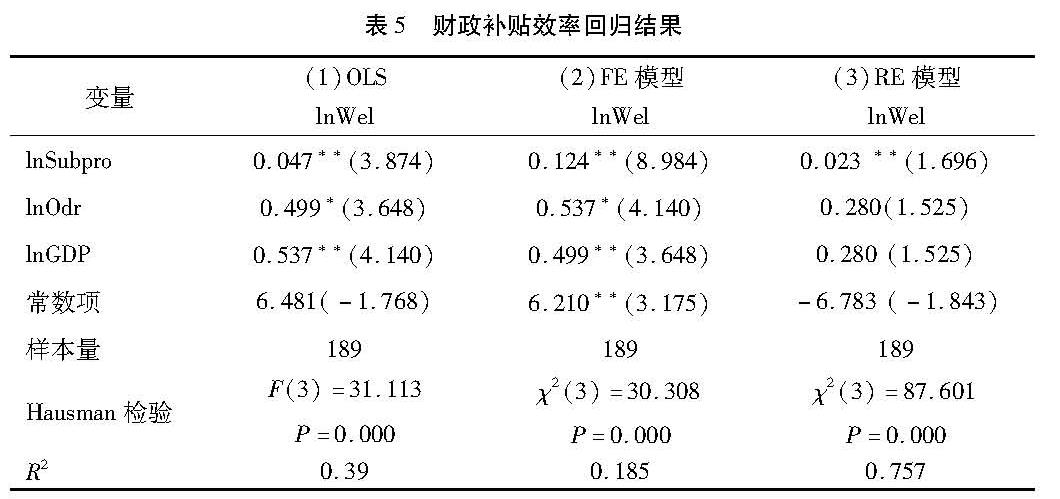
4.2 财政补贴效率对长期护理保险需求影响的分析(1)模型结果描述。在基本回归模型中,基于式(10),利用整理的面板数据,进行固定效应模型回归以及两阶段回归模型处理内生性问题检验财政补贴对养老保障水平的影响,回归结果如表5所示。财政补贴效率可以对养老保障水平有正向的促进作用,无论是全国地区或是东部与西部地区的核心变量均通过显著性检验。
财政补贴效率与养老保障水平显著正相关,即财政补贴可以有效提升居民的养老保障水平,增加长期护理保险的供给,提高长期护理保险需求,这也与假设2的结果一致。但这种影响效果随着地区人均GDP的改变存在着差异,也即是地区经济水平不同影响着财政补贴的效果。地区经济较为发达地区的居民有着较为迟缓的收入增长效应,而地区经济较为落后的居民有着明显的收入增长的效应。
(2)稳健性检验。为进一步验证财政补贴对养老保障水平的促进作用,表6利用医疗保健消费支出替代养老保障水平。从表6可见,财政补贴在模型0LS、固定效应回归结果均显著且为正,其与表5回归结果基本一致,进一步验证了假设2财政补贴效率促进养老保障水平增长的作用。回归结构显示,财政补贴效率会使养老保障水平增大,促进长期护理保险供给,进而增加长期护理保险需求。
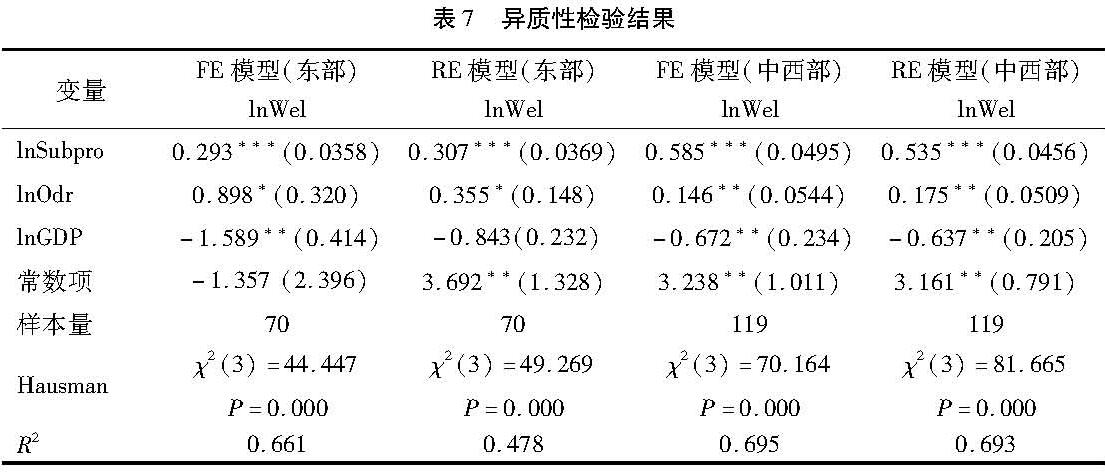
(3)异质性检验。为进一步检验财政补贴效率对长期护理保险需求的影响,将全部省份分为东、中、西三个部分,然后分别进行回归分析,回归结果如表7所示。在东部地区和中西部地区,财政补贴都效率都通过了显著性检验,东部地区的估计系数为0.293,而中西部地区估计系数为0.585,因此财政补贴效率对于长期护理保险需求的影响在中西部更加明显。
(4)模型结果分析。首先,从财政补贴效率(lnSubpro)对养老保障水平(lnWel)影响效果的实证分析研究中可知,财政补贴效率对养老保障水平显著且为正,可知财政补贴效率的提高可以有效提高长期护理保险供给。2020年9月国家医保局、财政部联合印发《关于扩大长期护理保险制度试点的指导意见》。试点基本都达到了预期的效果,促进相关产业和服务业的发展。在试点设立之前,老年人需要支付较为高昂的护理费用,让很多不富裕的家庭捉襟见肘。长护点的设立为参保人减轻负担,同时为就业做出巨大贡献。全国已经逐步建立补贴制度,帮助生活拮据的老年人渡过难关。向一些高龄的、行动不便的老年人发放福利津贴,解决他们的护理问题和生活问题。鼓励发展多种长护险产品,照顾到不同情况的老年人,为其提供全面的长护险服务。同时,指导意见对有关政策进一步明确,着眼于筹资的多样化和合理化。不断探索稳定可持续的长护险制度,优化政策性保险筹资结构。其次,财政补贴效率的作用效果是中西部地区优于东部,这是因为中西部地区相较于东部地区而言,经济水平较为落后,对财政补贴效率的刺激作用较为敏感,在财政补贴长期矫正之下,中西部地区长期护理保险需求强度的到大幅度提升,因此中西部地区长期护理保险消费提升的效果就优于东部地区。财政补贴对长期护理保险需求的影响在不同地区的差别主要体现在促进程度上。财政对低收入人群进行补贴,降低社会长期护理保险的筹资成本,进一步保证收支平衡,确保制度的平稳及可持续性[52]。长期护理保险财政补贴政策的实施,有效提高“兜底线、保基本”服务能力,减轻重点人群的长期照护基本负担,也有助于带动养老服务业整体发展,提高医疗、养老资源配置效率,与经济社会发展形成良性互动。政府对长期护理保险的政策支持可以使投保人降低支付长期护理保险的成本并且给投保人带来最大的效用。从而减少长期护理保险中的各类风险造成的经济损失。
5 结论和政策建议
5.1 结论长期护理保险的财务补贴问题关系到长期护理保险能否有效运行,所谓长期护理保险财政补贴,就是指由政府负责为长护险相关各项的开支提供和资金支持,更好地对患有残疾或慢性疾病而失能的人群提供长期护理服务。只有长护险财政补贴机制具有足够的科学性、合理性,才能延续长护险制度的生命力,让长护险蓬勃发展。完善长护险财政补贴政策,是促进合理使用资金,提高保费补贴效率的有效手段。同时,财政补贴对老年人有一定的激励作用,能够提高老年人参与的积极性,从而刺激消费。
实证结果表明,财政补贴对居民可支配收入有着显著的正向影响,从而提高长期护理保险需求; 财政补贴效率可以通过增加养老保障水平,使居民的长期护理保险需求得到提高。由于不同地区经济水平、财政收入水平人口结构等因素不同,财政补贴在不同地区具有差异,对长期护理保险需求的影响效果不同。进一步拓展发现,财政补贴在中西部比在东部有更好的促进效果,更能增加居民的长期护理保险需求。
5.2 政策建议(1)对于参保居民,政府应给予财政适度补贴,以降低长期护理保险的价格,减少居民参保的费用,增加居民的可支配收入,以此来提高长期护理保险需求。政府应积极向居民宣传长期护理保险,增加财政补贴,设立有益于居民的参保激励政策,以核心保障目标群体为重点补贴对象,使社会整体的效用实现最大化。(2)在政府承受范围内,可以适当提高财政补贴的比重,增加长护险的供给,提升服务品质,带动长护险的优质发展。合理的财政补贴比例能够使补贴效率最大化,长期护理保险更好地为解决我国失能老年人的照护问题服务,为根据新的政策要求调整和完善长期护理保险财政补贴体系提供参考,从而推动我国多层次医疗保障体系的发展。(3)财政补贴力度应依据不同地区的经济发展程度与居民的实际需求进行合理安排,在保障居民参保积极性的基础上兼顾公平原则。将长护险和长护险财政补贴制度互相结合起来,才能更好地规避风险,使老年人能够很好地应对失能风险,让晚年生活得以保障。基于政府充当的角色,政府应利用补贴强化其托底责任,有效地贯彻长护险的补贴政策。因此,在政府承受范围内,要创新长期护理保险服务补助政策,适当提高补贴支出额度。长护险拥有巨大的市场空间,同时还在生活质量提升方面有着重要的作用。老年人这个特殊群体对长护险有着迫切的需求,极大地带动了我国长护险的产生和发展。要想满足他们的需求,一定要建立较为完善的服务体系。通过构建包含财政补贴的筹资模式,创造公平、可持续的长护险体制。
- [1]文太林,孔金平.中国长期照护筹资与公共财政转型[J].行政论坛,2020,27(1):114-119.
- [2]荆涛,杨舒,朱海.政策性长期护理保险补贴制度研究[J].保险研究,2017(8):47-59.
- [3]丁志宏,魏海伟.中国城市老人购买长期护理保险意愿及其影响因素[J].人口研究,2016,40(6):76-86.
- [4]ELING M,GHAVIBAZOO O. Research on long-term care insurance: status quo and directions for future research[J].Geneva Papers on Risk and Insurance-Issues and Practice,2019,44(2):303-356.
- [5]荆涛,王靖韬,李莎.影响我国长期护理保险需求的实证分析[J].北京工商大学学报(社会科学版),2011,26(6):90-96.
- [6]GOTTLIEB D,MITCHELL O S. Narrow framing and long-term care insurance[J].Journal of Risk and Insurance,2020,87(4):861-893.
- [7]KLIMAVICIUTE J,PESTIEAU P,SCHOENMAECKERS J. Long-term care insurance with family altruism: theory and empirics[J].Journal of Risk and Insurance,2020,87(4):895-918.
- [8]HE A J, CHOU K L. What affects the demand for long-term care insurance? a study of middle-aged and older adults in Hong Kong[J].Journal of Applied Gerontology,2020,39(4):413-422.
- [9]曹信邦,陈强.中国长期护理保险需求影响因素分析[J].中国人口科学,2014(4):102-109,128.
- [10]杨翠迎,程煜.不同福利国家模式下长期护理保险制度及其费率结构比较[J].经济体制改革,2019(4):151-159.
- [11]雷晓康,冯雅茹.社会长期护理保险筹资渠道:经验借鉴、面临困境及未来选择[J].西北大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2016,46(5):108-115.
- [12]COURBAGE C,MONTOLIU-MONTES G. Estate recovery and long-term care insurance[J]. Journal of Public Economic Theroy,2020,22(4):949-972.
- [13]MCGARRY B E,GRABOWSKI D C. What do clinicians caring for aging patients need to know about private long-term care insurance?[J].Journal of the American Geriatrics Society,2019,67(10):2167-2173.
- [14]KONETZKA R T, HE D F,DONG J,et al. Moral hazard and long-term care insurance[J].Geneva Papers on Risk and Insurance-Issues and Practice,2019,44(2):231-251.
- [15]赵娜,陈凯.风险认知对长期护理保险购买意愿影响分析[J].保险研究,2015(10):84-95.
- [16]陈冬梅,袁艺豪.人口老龄化背景下我国长期护理保险需求的分析:以上海市为例[J].上海大学学报(社会科学版),2015,32(6):13-22.
- [17]王新军,李雪岩.长期护理保险需求预测与保险机制研究[J]. 东岳论丛,2020,41(1): 144-156.
- [18]XU X C,ZHANG L,CHEN L H,et al. Does COVID-2019 have an impact on the purchase intention of commercial long-term care insurance among the elderly in China?[J].Healthcare,2020,8(2):126-126.
- [19]FAICAL A,JOAN C F,RICHARD F. Uninsured by choice? a choice experiment on long term care insurance[J].Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization,2020,173(5):422-434.
- [20]刘璐,韩浩,马文杰.政府支农政策对农业保险需求的影响机制研究[J].农业经济问题,2016,37(10):31-40,110.
- [21]王晓红.精准扶贫视角下提升我国农业保险财政补贴效率研究[J].理论探讨,2020(1):102-107.
- [22]伍骏骞,任成一.市场价格、政府补贴与生猪价格指数保险需求——来自保险公司的大样本保单数据的证据[J].财经科学,2020(11):54-64.
- [23]KIM H,JEON B. Developing a framework for performance assessment of the public long-term care system in Korea:methodological and policy lessons [J]. Health Research Policy and Systems,2020,18(2):224-237.
- [24]曾之遥,李磊,刘木子云,等.农村居民养老保险财政补贴与农民家庭消费异质性——基于CHARLS数据的研究[J].财经理论与实践,2020,41(4):18-24.
- [25]刘中海.农村居民养老保险财政补贴的福利效应研究[J].社会保障评论,2020,4(1):146-159.
- [26]孙博文.我国农业补贴政策的多维效应剖析与机制检验[J].改革,2020(8):102-116.
- [27]刘汉成,陶建平.中国政策性农业保险:发展趋势、国际比较与路径优化[J].华中农业大学学报(社会科学版),2020(6):67-75,163-164.
- [28]FENG Z L,GLINSKAYA E. Aiming higher: advancing public social insurance for long-term care to meet the global aging challenge comment on "financing long-term care: lessons from Japan"[J].International Journal of Health Policy and Management,2020,9(8):356-359.
- [29]KIM H,KWON S. A decade of public long-term care insurance in South Korea: policy lessons for aging countries[J]. Health Policy,2021,125(1):22-26.
- [30]张伟,罗向明,曾华盛,等.政策性农业保险对不同群体的收入再分配效应[J].保险研究,2021(6):72-88.
- [31]朱青,卢成.财政支农政策与农民收入的实证研究——基于农业补贴的视角[J].暨南学报(哲学社会科学版),2020,42(3):67-83.
- [32]杜霞,周志凯.长期护理保险的参与意愿及其影响因素研究——基于陕西省榆林市的微观样本[J].社会保障研究,2016(3):41-50.
- [33]CHEN L H,ZHANG L,XU X C. Review of evolution of the public long-term care insurance(LTCI)system in different countries: influence and challenge[J].BMC Health Services Research,2020,20(1):1057-1057.
- [34]尹海燕.可持续的公共长期护理保险筹资机制:国外经验与中国方案[J].宏观经济研究,2020(5):166-175.
- [35]李长远,张会萍.发达国家长期护理保险典型筹资模式比较及经验借鉴[J].求实,2018(3):69-78,111.
- [36]刘文,王若颖.我国试点城市长期护理保险筹资效率研究——基于14个试点城市的实证分析[J].西北人口,2020,41(5):29-45.
- [37]PAMELA N,ALISON E C. The emerging market for supplemental long term care insurance in Germany in the context of the 2013 Pflege-Bahr reform[J].Health Policy,2017,121(6):588-593.
- [38]高旭东,李秉坤,尹航.政策性保险保费补贴机理与使用效率研究[J].商业研究,2018(4):54-60.
- [39]聂荣,沈大娟.影响农户参保农业保险决策的因素分析[J].西北农林科技大学学报(社会科学版),2017,17(1):106-115.
- [40]粟芳,方蕾.政策性农业保险补贴最优模式探析——基于“千村调查”的研究[J].财经研究,2017,43(11):140-153.
- [41]荆涛,杨舒,谢桃方.政策性长期护理保险定价研究——以北京市为例[J].保险研究,2016(9):74-88.
- [42]房珊杉,徐程,刘国恩,赵绍阳.城镇居民基本医疗保险参保决策中“搭便车动机”研究[J].保险研究,2012(7):111-120.
- [43]张跃华,庹国柱,符厚胜.市场失灵、政府干预与政策性农业保险理论——分歧与讨论[J].保险研究,2016(7):3-10.
- [44]贺娟.我国农业保险参保现状及应对措施——基于行为经济学视角[J].保险研究,2020(11):19-31.
- [45]胡平峰,郭忠兴.新农保农民缴费选择的经济理性:政府—农民关系嬗变的视角[J].江海学刊,2020(4):95-100,254.
- [46]张祖荣.我国农业保险保费补贴资金使用效果评价:方法与证据[J].财政研究,2017(8):101-111.
- [47]马学琳,夏李莹,应望江.普惠金融视角下农民商业保险消费与投资倾向——基于“千村调查”调研样本数据分析[J].西北农林科技大学学报(社会科学版),2021,21(5):85-94.
- [48]南永清,贺鹏皓,周勤.商业保险对居民消费影响研究——基于中国省级面板数据的经验证据[J].保险研究,2020(3):23-40.
- [49]方蕾,粟芳.中国农村保险市场发展:保险意识与政府保费补贴的替代作用——基于上海财经大学2015“千村调查”[J].经济管理,2016,38(10):140-154.
- [50]田勇,殷俊.“依托医保”长期护理保险模式可持续性研究——基于城乡居民与城镇职工的比较[J].贵州财 经大学学报,2019(2):91-101.
- [51]李佳.中国长期护理保险制度财政负担可持续性研究——基于 17 种试点方案测算[J]. 社会保障评论,2017,4(4): 53-71.
- [52]陈诚诚.长期护理保险试点地区筹资机制的实施现状与政策评述[J].学习与实践,2020(16):88-96.