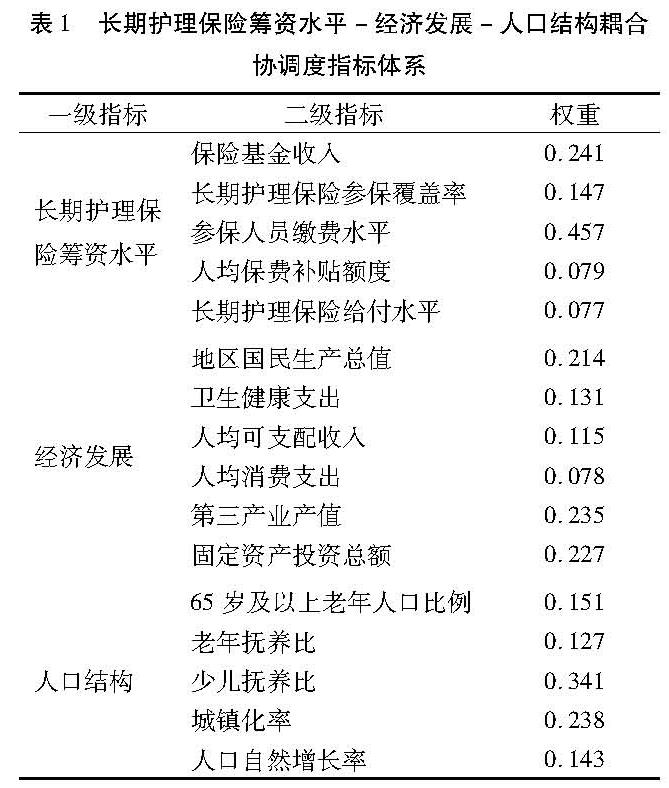
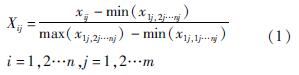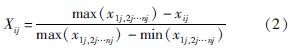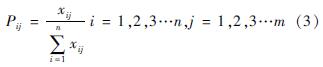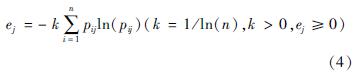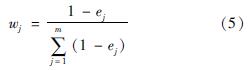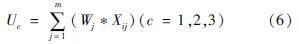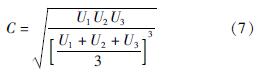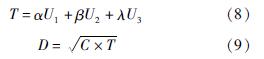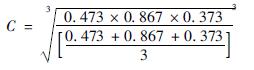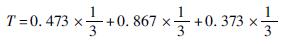3.1 两省长期护理保险发展现状分析
山东省是长期护理保险试点的重要联系省份,作为省会城市的青岛更是第一个试点城市,对于在全省范围内试行长期护理保险奠定了基础。目前山东省16个市都在试行长期护理保险。江苏省的苏州市和南通市都是第一批试点城市,苏州市目前正处于试点的第二阶段,逐步提高待遇标准,南通市的长期护理保险自实施以来,逐步形成了具有自身特色的制度体系。各试点城市的试点方案都是以《指导意见》为基础,然后结合自身经济发展情况和人口老龄化程度来制定的。试点方案的内容主要包括参保对象、筹资渠道、筹资来源以及服务形式等方面。
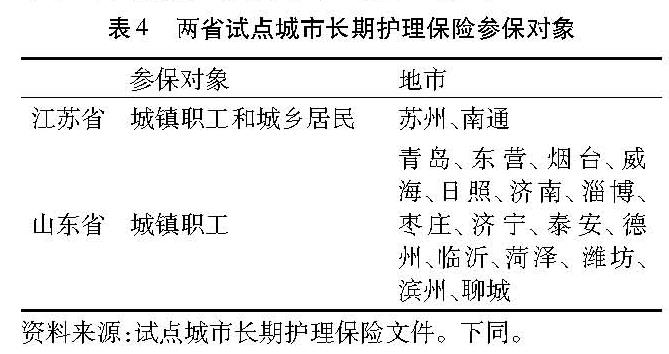
(1)参保对象。参保对象即是覆盖范围,参保对象覆盖的范围在一定程度上展现了长期护理保险的推广程度,也体现了长期护理保险基金的收支情况。试点阶段所规定的参保对象是根据基本医疗保险的参保人群来确定的。在18个试点城市中,参保对象可以分为两类:第一类是城镇职工基本医疗保险和城乡居民基本医疗保险的参保人群,包括苏州、青岛等试点城市; 第二类是城镇职工基本医疗保险参保人群,包括济南、淄博、枣庄等试点城市。各试点城市具体参保对象见表4。
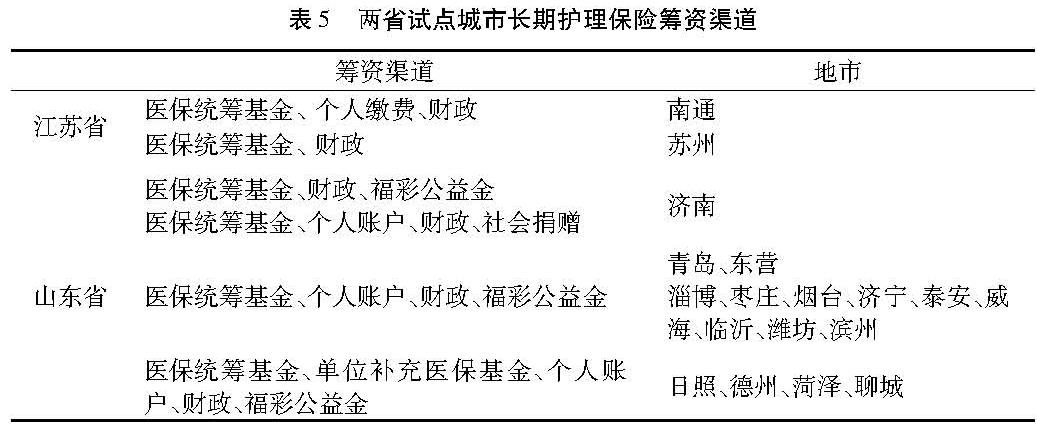
(2)筹资渠道。筹资渠道是指资金的来源,是长期护理保险基金的主要来源,保障长期护理保险制度的可持续运转。社会型长期护理保险主要包括医保统筹基金、个人账户、财政补贴这三个主要的筹资渠道。济南、淄博、烟台等试点城市还增加了福彩公益金这一筹资渠道,充实长期护理保险基金。日照、德州等试点城市还明确了单位的责任。各试点城市具体筹资渠道见表5。
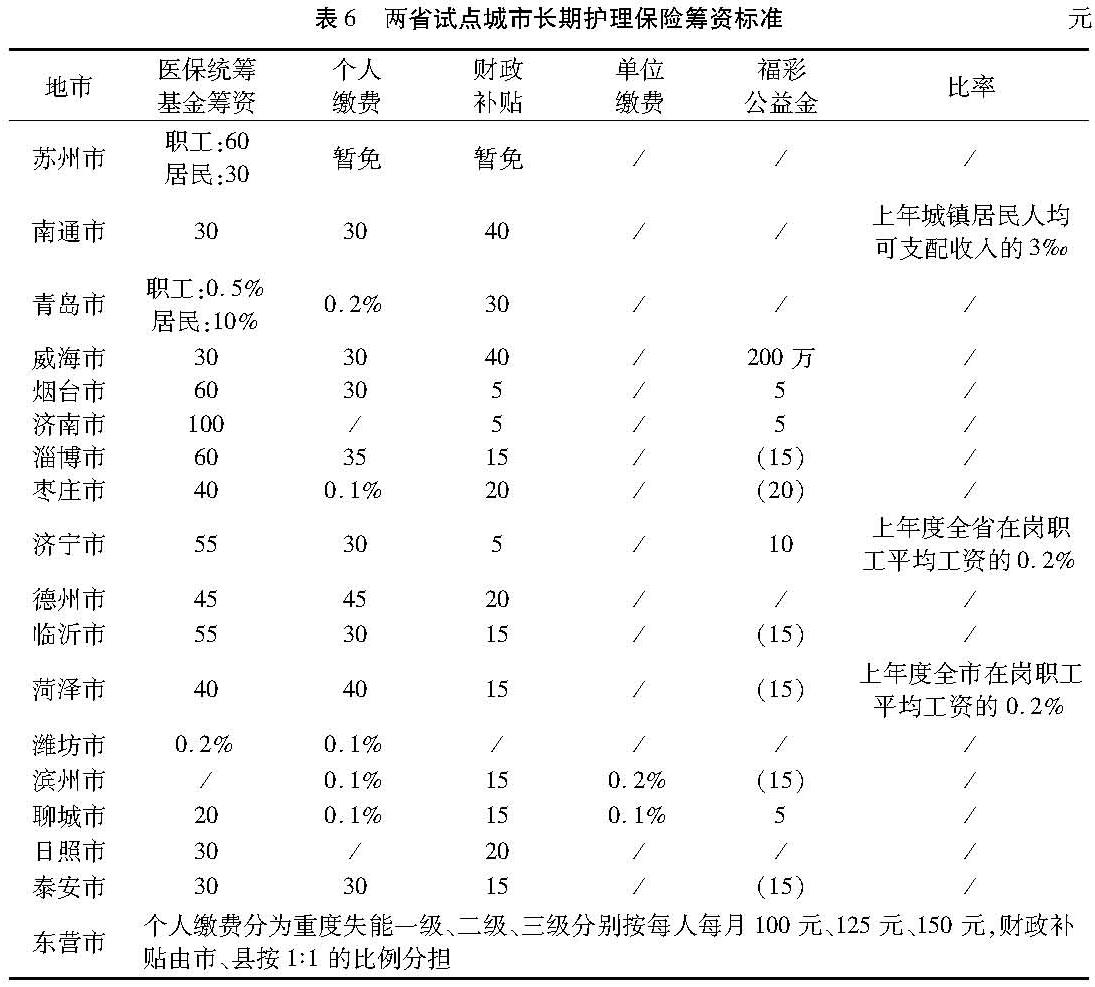
(3)筹资标准。筹资标准的制定主要是依据当地经济发展水平以及基金收支情况作出适当调整。两省试点城市的筹资标准主要有三类:一是定额筹资。苏州、烟台、济南、淄博、日照等试点城市采用的是固定标准进行筹资,从人均115~50元/年不等,其中济南最多为人均115元/年,日照最少为人均50元/年。二是定比筹资。青岛、潍坊、滨州等试点城市采用的是按比例筹资,比例各不相同,青岛分为职工和居民,分别从职工医疗保险和居民医疗保险基金中按不同比例划转,滨州明确了单位缴费比例为0.2%,个人为0.1%。三是混合筹资。南通、济宁、枣庄等试点城市采用的是定额和定比混合筹资,南通定额标准为人均100元/年,定比为上年城镇居民人均可支配收入的3‰左右确定。筹资标准具体情况可见表6。
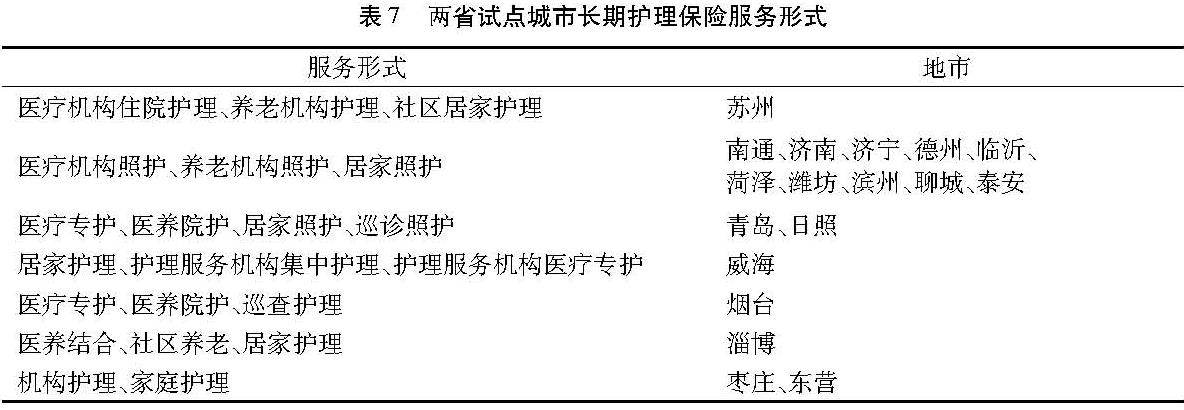
(4)服务形式。服务形式即长期护理保险为参保人群提供护理服务的方式,在18个试点城市中主要的服务形式是医疗专护、机构护理、居家护理,包括南通、济南、济宁等10个城市,苏州、青岛、淄博等城市还注重社区巡查护理,枣庄和东营目前只有机构护理和家庭护理。具体服务形式见表7。
3.2 实证结果分析
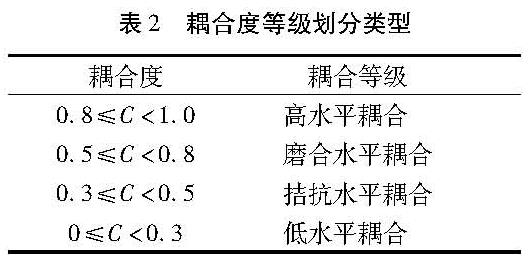
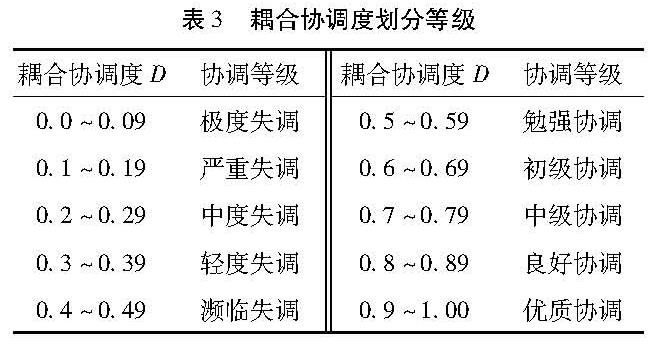
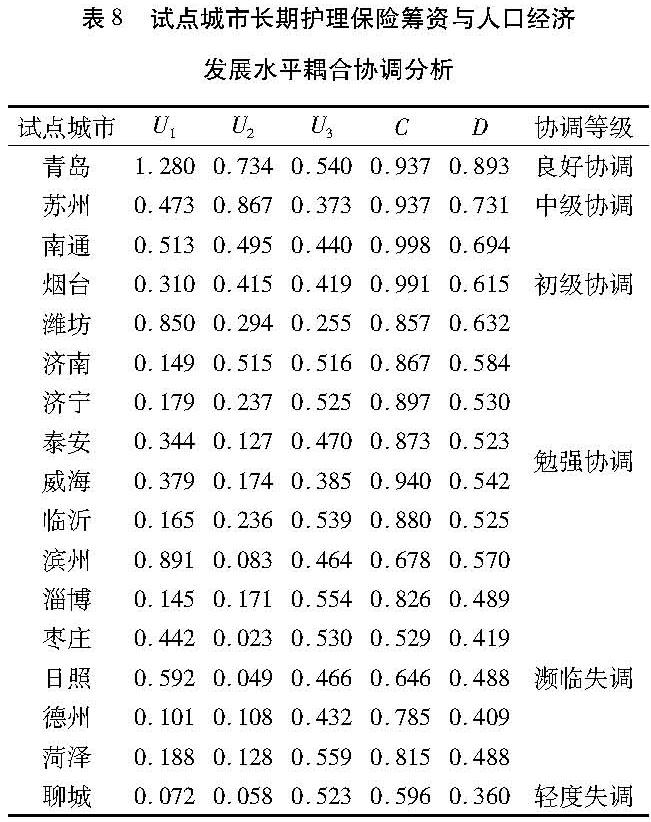
(1)试点城市耦合协调度整体水平。由于东营市未明确公布筹资标准,导致无法计算其基金收入,缴费水平和给付水平,从而无法确定其筹资水平的权重,因此文章对除东营市外的17个试点城市的耦合协调度进行分析,具体结果见表8。表8表明,这17个城市的耦合协调度在0.360~0.893,处在轻度失调-良好协调之间,平均为0.558,整体处于勉强协调阶段。说明本文选取的17个试点城市筹资水平、经济发展和人口结构之间的协调性还需加强,这是由于各试点城市的经济发展和人口结构不一导致政策不同,筹资水平自然也就不同。
根据式(6)~式(9)可以计算得出U1、U2、U3、C、D。以苏州市为例,根据式(6)计算出U1=0.473、U2=0.867、U3=0.373。计算过程如下:
U1=∑0.341×0.241+1×0.147+0.385×0.457+0×0.079+0.888×0.077
U2=∑1×0.214+1×0.131+1×0.115+1×0.078+1×0.235+0.413×0.226
U3=∑0.186×0.151+0.160×0.127+0.076×0.341+1×0.238+0.425×0.143
根据公式(7)计算出C=0.937,计算过程如下:
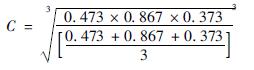
根据式(8)计算出T=0.571,计算过程如下:
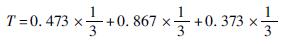
根据式(9)计算出D=0.731,计算过程如下:

根据以上计算过程就可得出各试点城市的耦合协调度,再通过表3划分协调等级(表8)。
表8 试点城市长期护理保险筹资与人口经济发展水平耦合协调分析
(2)各试点城市耦合协调度分析。根据表8协调等级从高到低的顺序对17个试点城市的耦合协调度进行总结分析。在17个试点城市中,青岛的耦合协调度最高,达到良好协调状态,从表8可以看出,其筹资水平和经济发展水平都处于较高水平,人口结构也比较协调。
苏州的耦合协调度为0.731,处于中级协调阶段,虽然其经济发展水平优于青岛,但是从筹资水平和人口结构的指标来看,青岛高于苏州,原因在于青岛市长期护理保险试点较早而且山东省是长期护理保险的重要联系省份,筹资标准等各项制度都比较完善。
南通、烟台、潍坊的耦合协调度处于(0.6,0.7)区间,为初级协调阶段。从耦合度来看,三个城市都属于高水平耦合; 从筹资水平的指标来看,潍坊>南通>烟台; 从经济发展和人口结构的综合评价指标来看,南通高于烟台和潍坊。
济南、济宁、泰安、威海、临沂、滨州的耦合协调度处于(0.5,0.59)区间,处于勉强协调阶段。从耦合度结果来看,滨州属于磨合水平耦合,其余为高水平耦合; 从筹资水平的指标来看,滨州优于其他城市,这是由于滨州在筹资标准中规定了单位缴费标准; 从经济发展的综合评价指标来看,济南优于其他城市; 从人口结构的综合评价指标来看,临沂优于其他城市。
淄博、枣庄、日照、德州、菏泽的耦合协调度处于(0.4,0.49)区间,为濒临失调阶段,从筹资水平的综合评价指标来看,日照高于其他城市; 从经济发展的综合评价指标来看,淄博的经济发展水平高于其他城市; 从人口结构的综合评价指标来看,5个城市的人口结构差距不大。
聊城的耦合协调度为0.360,处于轻度失调阶段。从表8中可以看出,其筹资水平和经济发展评价指标都远远低于其他城市,特别是与青岛差距较大。这是由于其覆盖率和给付水平较低,筹资水平和经济发展与人口结构发展水平不匹配。