(Palace History Department, The Palace Museum, Beijing, 100009, China)
urban planning; capital city planning; Luoyi of the Western Zhou Dynasty; modeling heaven and earth
DOI: 10.15986/j.1008-7192.2022.06.007
备注
引言
中国古代哲学中的“仰观俯察”精神,投射于城市规划领域,形成了城市规划史上独特的“象天法地”传统。鉴于古代天文学在政治和文化中的崇高地位,历代文献关于古代城市“象天法地”规划的记载非常可观,从中可以梳理出一条发展和变化的脉络。概括而言,“象天法地”规划萌发于商、周,兴盛于秦、汉,成熟于隋、唐,集大成于元、明、清。本文将回到西周初年这个关键节点,探讨“象天法地”规划理论的成型及其在都城雒邑营建中的表现。具体来说,讨论雒邑规划的四个问题:(1)规划思想:武王对雒邑规划的构想是“依天室,定天保”,“天室”究竟是天文要素还是地理要素?(2)规划选址:雒邑选址有“土中”“南望过于三涂,北望过于有岳,顾瞻过于河,宛瞻于伊洛,无远天室”及“洛汭”等说,其对应的地理范围究竟如何?(3)规划时间:雒邑规划从“二月乙未”持续到“三月甲子”,其中又以“三月庚戌”至“三月甲寅”为期五天的“攻位”环节最为关键,选择上述时间开展都城规划有何特殊含义?(4)规划布局:“攻位”的具体内容为“立城郛”“制郊甸”“分县郡”“居众民”“设丘兆”“建大社”“位五宫”“定建筑”,大致对应今日国土规划、区域规划、城市规划和建筑设计的内容,召公采取了何种空间组织模式得以在短期内实现多层次的空间规划?对上述问题的探索,将揭示雒邑规划的“象天法地”思想蕴含及实施方法。
1 相关材料
有关西周雒邑的营建,在青铜器铭文和历史文献中有着丰富的记载。材料中的“洛邑”“洛师”“大邑”“新邑”“新京”“新邑洛”“成周”“洛”等均指“雒邑”[1]。成王时期的青铜器“何尊”上刻铭文“唯武王既克大邑商,则廷告于天,曰:‘余其宅兹中国,自之乂民。'”证实了定都雒邑的历史事实(图1)。
历史文献则涉及《尚书》“召诰”“洛诰”,《逸周书》“度邑解”“作雒解”“明堂解”,以及《史记》“周本纪”“鲁周公世家”等篇。现分三类辑录如下。
第一类,记载了雒邑营建的背景和建都思想,如《史记·周本纪》:“武王征九牧之君,登豳之阜,以望商邑。武王至于周,自夜不寐。周公旦即王所,曰:‘曷为不寐?'王曰:‘……我未定天保,何暇寐!'王曰:‘定天保,依天室……自洛汭延于伊汭,居易毋固,其有夏之居。我南望三涂,北望岳鄙,顾詹有河,粤詹雒、伊,毋远天室。'成王在丰,使召公复营洛邑,如武王之意。周公复卜申视,卒营筑,居九鼎焉。曰:‘此天下之中,四方入贡道里均。'”[3]122-133又如《史记·鲁周公世家》:“成王七年二月乙未,王朝步自周,至丰,使太保召公先之雒,相土。其三月,周公往营成周雒邑,卜居焉,曰:‘吉',遂国之。”[3]1515-1519以及《逸周书·度邑解》:“王曰:‘我图夷兹殷,其惟依天室,其有宪命,求兹无远虑。天有求绎,相我不难。自洛汭延于伊汭,居阳无固,其有夏之居。我南望过于三途,我北望过于有岳,顾瞻过于河,宛瞻于伊洛,无远天室。'”[4]479-483
第二类,记载了雒邑营建的步骤和召公、周公的工作内容,如《尚书·召诰》:“惟二月既望,越六日乙未,王朝步自周,则至于丰。惟太保先周公相宅。越若来三月,惟丙午朏。越三日戊申,太保朝至于洛,卜宅。厥既得卜,则经营。越三日庚戌,太保乃以庶殷攻位于洛汭。越五日甲寅,位成。若翼日乙卯,周公朝至于洛,则达观于新邑营。越三日丁巳,用牲于郊,牛二。越翼日戊午,乃社于新邑,牛一,羊一,豕一。越七日甲子,周公乃朝用书命庶殷侯甸男邦伯。厥既命殷庶,庶殷丕作。”[5]285又如《尚书·洛诰》:“周公拜手稽首曰:‘……予惟乙卯朝至于洛师。我卜河朔黎水,我乃卜涧水东、瀍水西,惟洛食; 我又卜瀍水东,亦惟洛食。伻来以图及献卜。'”[5]294
第三类,记载了雒邑营建的空间布局模式,如《逸周书·作雒解》:“周公敬念于后,曰:‘……乃作大邑成周于土中。立城方千七百二十丈,郛方七十二里。南系于雒水,北因于郏山……大县立城,方王城三之一,小县立城,方王城九之一……乃设丘兆于南郊……乃建大社于国中……乃位五宫:太庙、宗宫、考宫、路寝、明堂。'”[4]524-542
从上述材料来看,雒邑营建主要涉及四个关键人物:(1)武王:提出定都雒邑的构想,划定都城的大致范围;(2)成王:武王之子,继承武王遗愿,是雒邑营建时期的执政者;(3)召公:武王至成王时期的重要辅臣,时任太保,负责雒邑营建中的“卜宅”“经营”“攻位”等步骤;(4)周公:武王之弟,同样是武王至成王时期的重要辅臣,负责雒邑营建中的“观邑”“郊祀”“社祀”“丕作”等步骤。
2 规划选址
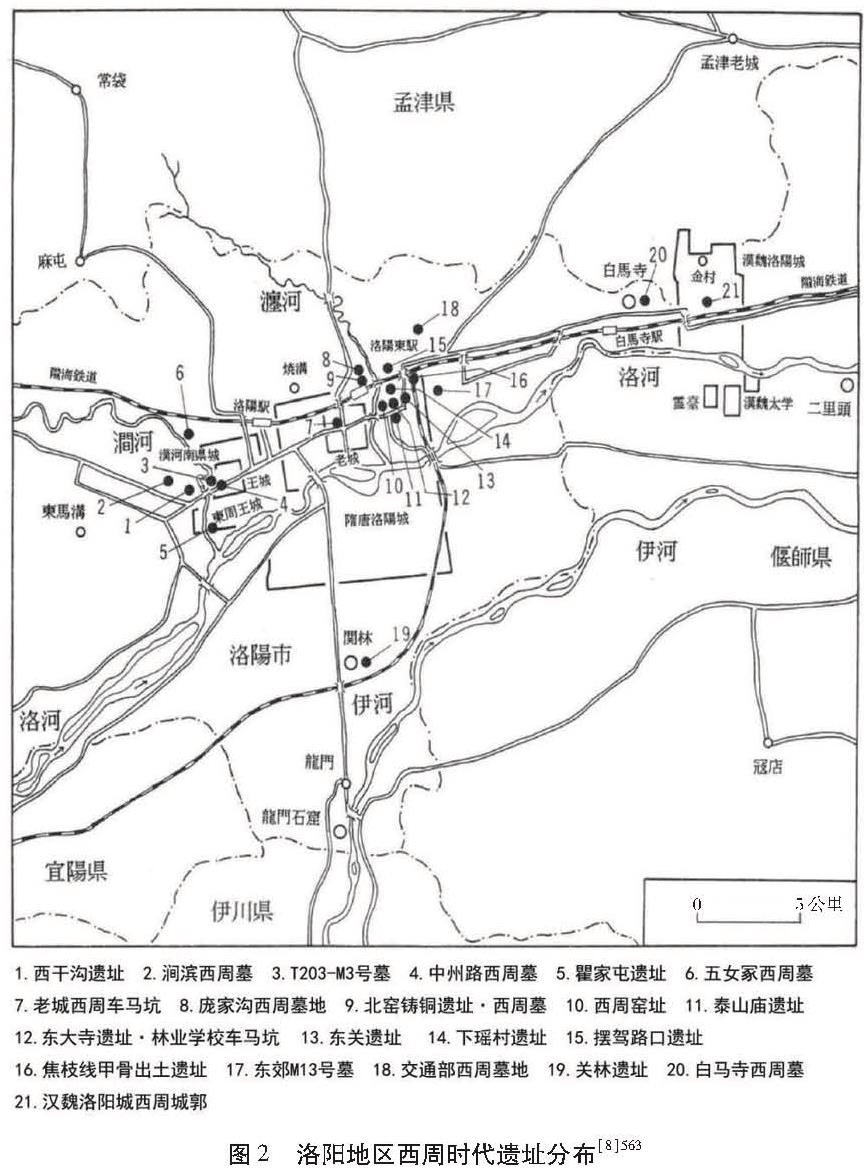
虽然雒邑遗址在考古中尚无定论,但多年的历史地理和考古研究仍然积累了不少成果,厘清了西周时期伊水、洛水、涧水、瀍水等主要河流的走向[6],洛阳地区古代城址的空间演变[7],以及西周遗址的总体分布等[8],为进一步揭示西周雒邑的位置和布局提供了有力线索(图2)。
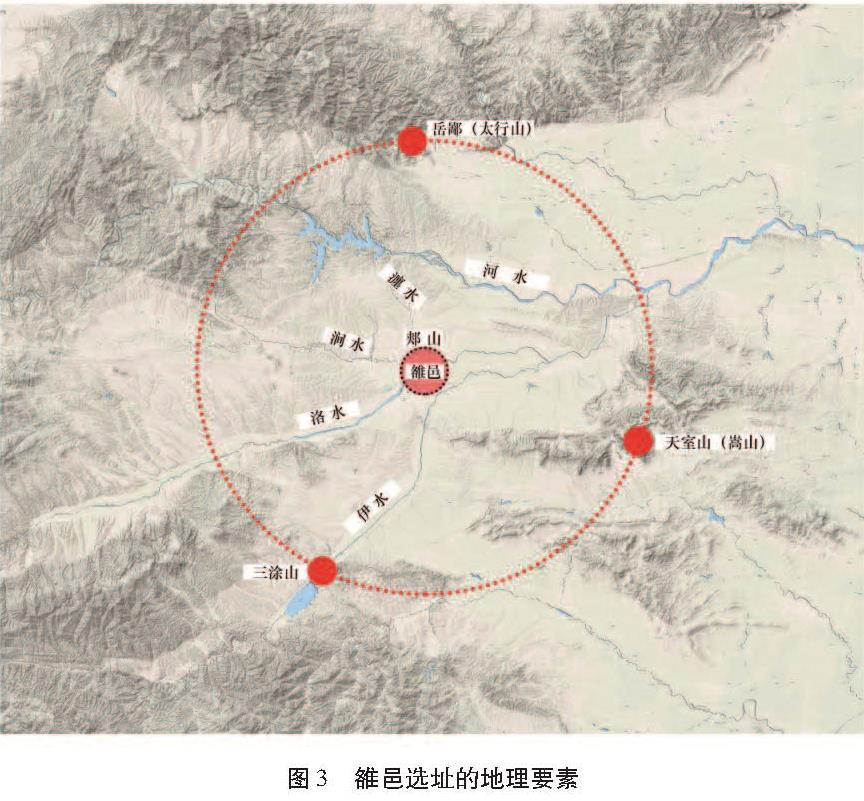
依据文献,雒邑选址在空间上分为三个圈层:(1)最大的圈层,是国土的中心。《逸周书·作雒解》记载“乃作大邑成周于土中”,《史记·周本纪》记载“此天下之中,四方入贡道里均”,都是指将都城置于“天下之中”。(2)中间的圈层,是都城的腹地。在《史记·周本纪》中由武王拟定,“我南望三涂,北望岳鄙,顾詹有河,粤詹雒伊,毋远天室”。《逸周书·度邑解》也有类似表述。即南至三涂、北至岳鄙、西至天室的三山界定的范围,其间有河水、洛水、伊水等流经。(3)最小的圈层,是都城的边界。从《尚书·洛诰》记载的周公卜地来看,“我乃卜涧水东、瀍水西,惟洛食; 我又卜瀍水东,亦惟洛食”。雒邑应占据涧水东、瀍水西以及瀍水东的两个地块; 从《逸周书·作雒解》“南系于雒水,北因于郏山”和《尚书·召诰》“攻位于洛汭”来看,雒邑选址还应靠近洛水。
综上,雒邑选址应在洛水、涧水、瀍水交汇的附近,这与前述洛阳地区西周遗址的分布特征也相吻合(图3)。
3 规划时间
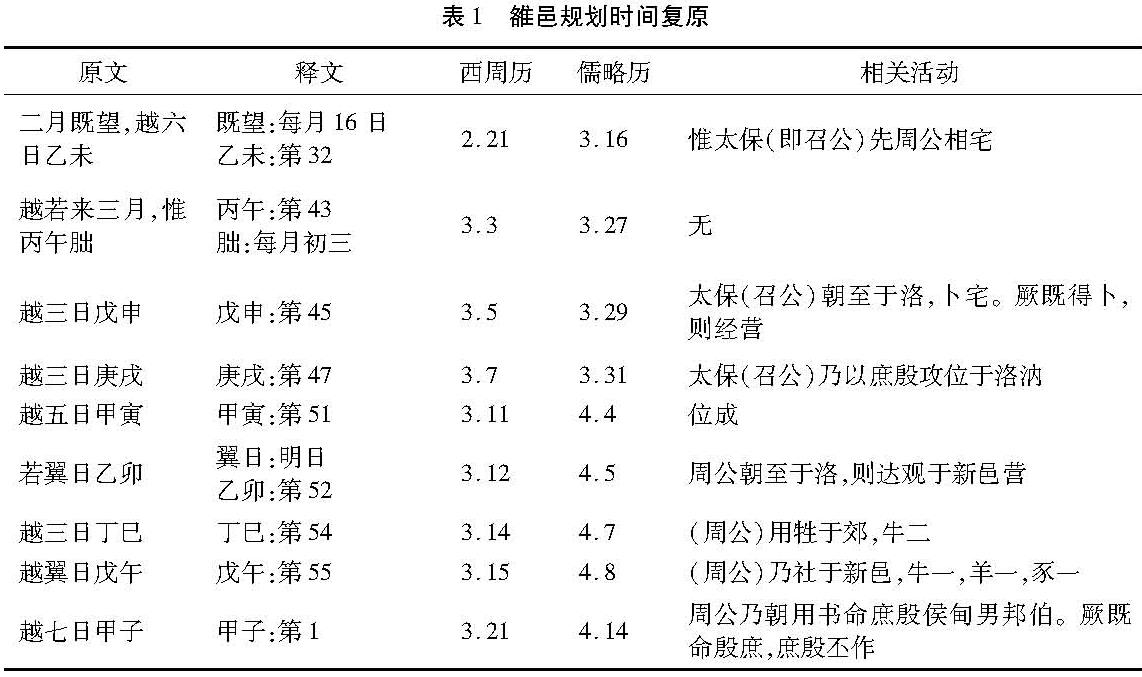
仔细阅读《尚书·召诰》,“攻位”介于“召公卜宅”和“周公祭祀”之间,其内容应包括都城选址与主要功能区布局,正是今日城市规划的主要内容[9]。 “攻位”从“三月庚戌”持续到“三月甲寅”,才宣告“位成”。那么,“攻位”一共持续了多少天?又为什么选择这几天呢?鉴于《尚书·召诰》的记载非常翔实,下文即对照《西周纪年》等研究,还原《尚书·召诰》所涉及的具体日期(表1)。
从表1可以看到,雒邑规划从西周历3月5日(戊申)召公到达雒邑开始,一直持续到3月21日(甲子)周公率殷遗民营建为止,共计17日。其中3月7日(庚戌)至11日(甲寅)为“攻位”,耗时5天。刘启益《西周纪年》的研究将雒邑营建时间定在成王七年,对应公元前1062年[10]。张培瑜《三千五百年历日天象》的复原研究显示,公元前1062年的春分点在3月31日23时20分,当日也为庚戌日[11]。虽然西周历法的研究尚存争议,但“攻位”起始日极有可能就是春分日,因为前后两个庚戌日各相差60天,不可能同时满足“三月”的条件。将“攻位”时间选择在春分日的事实,揭示出西周雒邑规划“象天法地”的可能。
《逸周书·度邑解》有“其惟依天室,其有宪命,求兹无远虑”的记载,说明雒邑营建的背后,存在“依天室”——“有宪命”——“无远虑”的逻辑,即将都城规划“依天室”与“得天命”联系起来。从这个角度出发,可以重新审视“天室”的含义[12]。在上述引文之后,紧接着是“天有求绎,相我不难”一句。目前通行的解释是:“绎”通“怿”,即“悦”,取“高兴”之义。但其实“绎”字还有另一个解释,即“灵星之尸”,见于《毛诗正义》:“丝衣,绎宾尸也。高子曰:‘灵星之尸也。'” [13]749这一解释非常关键,说明在汉代以前,“绎”字还有天文学上的含义。灵星,即角宿的天田二星,位于黄道平面和赤道平面的交点,是春分日的代表。《史记·天官书》引《石氏星经》云:“左角为天田,右角为天门也。”[3]1297天田是东方七宿组成的“东宫苍龙”的“左角”,《汉书·郊祀志》引张晏曰:“龙星左角曰天田,则农祥也,辰见而祭之。”天田主农祥,汉高祖时曾“令天下立灵星祠,常以岁时祠以牛”[14]1211-1212。
天文复原法在历史年代学的相关课题中发挥了巨大作用,如夏商周断代工程中著名的“武王伐纣”问题。本文借鉴这一研究方法,使用天文复原软件Stellarium,以雒邑遗址所在的洛阳地区(N 34°41', E 112°27')为基准点,复原上文求得的“攻位”日春分点(前1062年3月31日23时20分)的历史天象。从图4可以看到,天田二星此时正位于南中天,与北极的连线构成一条南北方向的轴线。
接下来的问题是,为何周人选取灵星(绎星)为雒邑轴线的重要参考?从周制中可一窥端倪。《诗经·大雅·生民》和《史记·周本纪》均记载“后稷”为周人始祖。而周制以“灵星”配“后稷”:“汉兴八年,有言周兴而邑,立后稷之祀,于是高帝令天下立灵星祠。言祠后稷而谓之灵星者,以后稷又配食星也。旧说,星谓天田星也。一曰,龙左角为天田官,主谷。祀用壬辰位祠之。壬为水,辰为龙,就其类也。”[15]3204在天人相应观念影响下,周人通过祭祀灵星来达到祭祀祖先的目的。而都城雒邑的规划,推测便是以春分点灵星所在方位来确定都城轴线的指向。关于春分点这一时刻的选择,也不是随意的。春分时节太阳直射赤道,平分昼夜,不仅在天文学上具有重要意义,也标志着中国古代大部分地区农耕时节的开始。周人重农,后稷正是因为“好耕农”而被帝尧封为“农师”。
在稍晚时期的文献中,依然可以看到这种以特定时刻星象确定都城规划布局的手法。《诗经·鄘风·定之方中》有:“定之方中,作于楚宫。揆之以日,作于楚室。”[16]84-85《国语·周语》引《夏令》曰:“营室方中,土功其始。”[17]31这里的“定”指“营室”星,即楚宫的规划是通过“夜观营室”和“昼观日”来确定的。正如《考工记·匠人建国》所言:“昼参诸日中之景,夜考之极星,以正朝夕。”[18]110从《周礼》中还可以看到“冯相氏”“保章氏”“土方氏”等与此相关的职官[19]378-379,487。
4 规划布局
明确“攻位”当日“象天”以定轴线之后,可以进一步推测余下四天的工作。一般来说,轴线确定之后,应当开展都城的布局。这一部分,以《逸周书·作雒解》的记载最为详尽,完整保留了雒邑营建所采取的空间组织模式。从内容来看,营城部分为四个层次,大致对应今日的国土规划、区域规划、城市规划和建筑设计。其中“制郊甸”“分县郡”“居众民”是国土层面; “立城郛”是区域层面; “设丘兆”“建大社”“位五宫”是城市层面; 而“定建筑”则是建筑层面。
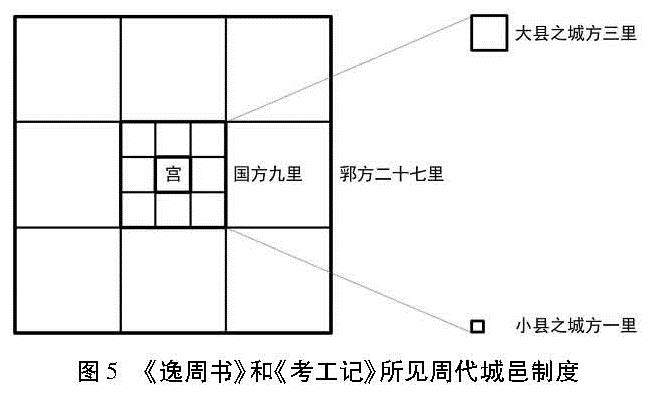
值得注意的是,相关文献在描述王郛、王城、大县之城、小县之城、明堂等不同规模的空间时,均使用了统一的规划设计模式。如《逸周书·作雒解》中“郛方七十二里”一句,不同版本有“七十里”“七百里”“七十二里”“十七里”等说。对此,清代经学大师孙诒让指出:“窃疑当为方二十七里,乃三城方之数也。……王宫方九百步,即三里,城内包宫垣距城面各三里,并之为城方九里。郛内包城,城距郛面亦各九里,并之为郛方二十七里也。”[4]526-528这一观点是颇有见地的。从《考工记·匠人营国》记载的都城规制来看,“国”是九宫格局,每宫方三里,宫城居中:“匠人营国,方九里,旁三门。国中九经九纬,经涂九轨,左祖右社,面朝后市,市朝一夫。”[18]112
而据《逸周书·作雒解》的记载,“郛”同样是九宫格局,每宫方九里,“国”居其中。同时,“大县立城,方王城三之一,小县立城,方王城九之一”。即大县之城方三里,小县之城方一里(表3)。如此,建立起了一套层级分明、制度严整的“九宫嵌套”的城邑体系(图5)。
在建筑层面,这种“九宫”模式依然存在。以“位五宫”中的“明堂”为例,《逸周书·明堂解》记载:“明堂方百一十二尺,高四尺,阶广六尺三寸。室居中方百尺,室中方六十尺,户高八尺,广四尺。东应门,南库门,西皋门,北雉门。东方曰青阳,南方曰明堂,西方曰总章,北方曰玄堂,中央曰太庙。左为左介(个),右为右介(个)。”[4]710-716
文献所载的宗周明堂,时代早于雒邑明堂,可作为雒邑明堂的设计参考。据此数据复原的西周明堂平面,与考古出土的东周漆器上的明堂图案比较,吻合程度非常高[20-21](图6)。
如图6所示,西周明堂的布局仍然是“九宫”模式的变体,这说明当时在国土、区域、城市、建筑等不同尺度,均使用一套相同的空间组织模式,即“九宫”之法。在《周礼》中,这套方法也被称为“形体之法”,有“遂人”“形方氏”等职官[19]223,489。到了《汉书·艺文志》,则被称为“形法”,来源于“九州之势”[14]1775。因此“九宫”模式的渊源,可追溯至“茫茫禹迹,画为九州”这一早期空间规划行为。传说“大禹治水”采用了“洛书”的空间模式:“《洛书》者,禹治水时,神龟负文而列于背,其数至九,禹遂因而第之,以成九类。”[22]165而“洛书”的出现地,恰好位于雒邑选址的“洛汭”:“仓颉为帝南巡,登阳虚之山,临于玄扈洛汭之水,灵龟负书,丹甲青文,以授之。”[23]486作为历史上“九宫”模式的诞生地,雒邑规划极有可能受到地方传统的影响。这套“九宫”之法,在西周时期进一步衍生,成为名副其实的“地法”,深刻影响了城市、建筑等领域,形成了一整套覆盖从天下到国家、从国家到城市、从城市到建筑等不同尺度的空间规划设计模式。
5 规划复原
结合前述洛阳地区山水格局和西周遗址的分布,做一大胆猜测,雒邑选址应在洛水、涧水、瀍水交汇的附近,都城轴线朝南,空间布局为内外城嵌套的形式,其内城“方九里”,外城“方二十七里”。按照西周一里约为480米推算[24]68-72,西周雒邑的轴线很可能与隋唐洛阳的轴线位置重合,直指南面的伊阙。相应地,雒邑内城大致位于隋唐洛阳城的宫城和皇城范围,外城南面与隋唐洛阳外城南墙重合。依此划定的雒邑范围,基本涵盖了洛阳地区的西周遗址,但究竟情况如何,还有待考古发掘工作的进一步开展。
6 结 语
以历史文献和考古材料为基础,揭示西周雒邑规划的“象天法地”思想蕴含。研究显示,雒邑的“象天法地”规划,早在武王时期就已拟定基本原则,但直到成王时期才真正实施。第一阶段由太保召公主持,分为相宅、卜宅、攻位三步。其核心步骤是“攻位”,耗时5天,共两部分内容:一是“拟定中轴线”; 二是“组织空间布局”。在“拟定中轴线”环节,运用“象天”规划手法,选取春分点这一特殊时刻星象,以“绎星”(角宿天田二星)和北极的连线,定下都城中轴线。在“组织空间布局”环节,采取“九宫”模式,划分城、郛范围,制定郡、县之城的规模,确定丘兆、大社、太庙、宗宫、考宫、路寝、明堂等核心建筑的位置和形制。“九宫”模式上可追溯至“洛书”,是“大禹治水”后划分“九州”的模式,被后世奉为“形法”,是古代空间组织的原型。雒邑规划吸纳了这一模式,从“法地”角度,对国土、区域、都城、建筑等不同空间采取统一的划分方式,形成“九宫嵌套”的空间体系。召公的工作完成后,由周公主持占卜、郊社祭祀和具体的营建活动。
贺业钜对《考工记》“匠人营国”制度的研究显示,西周初期是中国古代城市规划制度形成的时代。本研究进一步揭示出西周雒邑的选址和布局还蕴含了“象天法地”特征,可以推测,这一时期同样也是中国古代“象天法地”规划思想和方法的确立时期。雒邑规划以特定时刻天象拟定都城中轴线位置,以“九宫”模式组织城邑空间布局,树立了中国古代都城“象天法地”规划的典范,在秦咸阳、西汉长安、东汉雒阳、隋大兴-唐长安、隋唐洛阳,元大都,明清北京的规划中均有所继承和创新。
西周雒邑的“象天法地”规划手法,相对来说已经成型。以雒邑为出发点,可进一步追溯“象天法地”规划的早期案例。《尚书·尧典》记载了帝尧时期对“四仲中星”鸟、火、虚、昴的观测; 《左传》《国语》有“辰为商星、参为晋星”“商主大火”等记载。商人同时还是营城高手,目前考古认定的郑州、偃师、洹北三座商城,大致覆盖了公元前1600-1300年,都非常规整且存在南偏西方向的中轴线。这是否与当时“商星”的位置相关,是否与西周雒邑取“绎星”与北极连线的方法相同,值得进一步探讨。
西汉长安的规划思想被张衡精辟地总结为“览秦制、跨周法”,何为“秦制”、何为“周法”?根据《史记·秦始皇本纪》的记载和相关研究,都城咸阳规划主要表现为“为复道,自阿房,渡渭,属之咸阳,以象天极、阁道绝汉、抵营室也”的“象天”特征和“表南山之颠以为阙”的“法地”特征。西周雒邑和秦咸阳规划所共有的“象天法地”蕴含,可以为解读西汉长安的规划思想和空间布局提供更加广阔的思路。
- [1]钟春晖. 天下观念与周初之建都雒邑[C]//清华大学历史系. 社会·经济·观念史视野中的古代中国. 北京: 国际青年学术会议暨第二届清华青年史学论坛, 2010:367-377.
- [2]段德新. 国宝何尊与“中国”[J]. 文博, 2005(6):30-31.
- [3]司马迁. 史记[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 2013.
- [4]黄怀信, 张懋镕, 田旭东. 逸周书汇校集注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2007.
- [5]李民, 王健. 尚书译注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2000.
- [6]叶万松, 张剑, 李德方. 西周洛邑城址考[J]. 华夏考古, 1991(2):70-76.
- [7]李久昌. 国家、空间与社会: 古代洛阳都城空间演变研究[M]. 西安: 三秦出版社, 2007.
- [8]饭岛武次. 洛阳西周时代的遗址与成周、王城[J]. 胡明明, 译. 考古学研究, 2003:557-571.
- [9]郭璐. 中国早期都邑规划中的“位”[J]. 城市规划, 2021(12):77-83.
- [10]刘启益. 西周纪年[M]. 广州: 广东教育出版社, 2002.
- [11]张培瑜. 三千五百年历日天象[M]. 郑州: 大象出版社, 1997.
- [12]林沄. 天亡簋“王祀于天室”新解[J]. 史学集刊, 1993(3):24-29.
- [13]毛公,郑玄,孔颖达. 毛诗正义[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 1990.
- [14]班固. 汉书[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 2013.
- [15]范晔. 后汉书[M]. 李贤, 等, 注.北京: 中华书局, 1965.
- [16]程俊英. 诗经译注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2016.
- [17]韦昭. 国语[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2008.
- [18]闻人军. 考工记译注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2008.
- [19]杨天宇. 周礼译注[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2004.
- [20]曹春萍. “四阿重屋”探考[J]. 华中建筑, 1996(1): 50-55.
- [21]杨鸿勋. 明堂泛论——明堂的考古学研究[C]//中国建筑学会建筑史学分会, 清华大学建筑历史与文物建筑保护研究所. 营造第一辑. 北京: 第一届中国建筑史学国际研讨会,1998: 3-96.
- [22]孔安国,孔颖达. 尚书正义[M]. 上海: 上海古籍出版社, 1990.
- [23]王国维. 水经注校[M]. 上海: 上海人民出版社, 1984.
- [24]丘光明, 邱隆, 杨平. 中国科学技术史:度量衡卷[M].北京: 科学出版社, 2001.



![图6 《逸周书·明堂解》复原平面与东周漆画中的明堂(来源:右图文献[20]53)](2022年06期/pic13.jpg)
